A risk practitioner has identified that the agreed recovery time objective (RTO) with a Software as a Service (SaaS) provider is longer than the business expectation. Which of the following is the risk practitioner's BEST course of action?
Which of the following activities should be performed FIRST when establishing IT risk management processes?
Which of the following BEST enables an organization to determine whether external emerging risk factors will impact the organization's risk profile?
Which of me following is MOST helpful to mitigate the risk associated with an application under development not meeting business objectives?
After conducting a risk assessment for regulatory compliance, an organization has identified only one possible mitigating control. The cost of the control has been determined to be higher than the penalty of noncompliance. Which of the following would be the risk practitioner's BEST recommendation?
The operational risk associated with attacks on a web application should be owned by the individual in charge of:
Which of the following is the BEST reason to use qualitative measures to express residual risk levels related to emerging threats?
Which of the following is MOST important to determine when assessing the potential risk exposure of a loss event involving personal data?
Which of the following is MOST important to consider when determining the value of an asset during the risk identification process?
Which of the following issues found during the review of a newly created disaster recovery plan (DRP) should be of MOST concern?
Which of the following is the BEST risk management approach for the strategic IT planning process?
Which of the following presents the GREATEST risk to change control in business application development over the complete life cycle?
Which of the following would provide the MOST comprehensive information for communicating current levels of IT-related risk to executive management?
When testing the security of an IT system, il is MOST important to ensure that;
Which of the following practices BEST mitigates risk related to enterprise-wide ethical decision making in a multi-national organization?
A key risk indicator (KRI) threshold has reached the alert level, indicating data leakage incidents are highly probable. What should be the risk practitioner's FIRST course of action?
An organization has initiated a project to launch an IT-based service to customers and take advantage of being the first to market. Which of the following should be of GREATEST concern to senior management?
Which of the following BEST prevents unauthorized access to customer personal data transmitted to third-party service providers?
Which of the following risk impacts should be the PRIMARY consideration for determining recovery priorities in a disaster recovery situation?
Which of the following is necessary to enable an IT risk register to be consolidated with the rest of the organization’s risk register?
A risk practitioner has established that a particular control is working as desired, but the annual cost of maintenance has increased and now exceeds the expected annual loss exposure. The result is that the control is:
Within the risk management space, which of the following activities could be
delegated to a cloud service provider?
Which of the following BEST indicates the effectiveness of anti-malware software?
In an organization that allows employee use of social media accounts for work purposes, which of the following is the BEST way to protect company sensitive information from being exposed?
Which of the following is the BEST way to ensure data is properly sanitized while in cloud storage?
The BEST way to obtain senior management support for investment in a control implementation would be to articulate the reduction in:
Which of the following is MOST useful when performing a quantitative risk assessment?
Which of the following is the MOST effective way 10 identify an application backdoor prior to implementation'?
A failed IT system upgrade project has resulted in the corruption of an organization's asset inventory database. Which of the following controls BEST mitigates the impact of this incident?
An organization has implemented a cloud-based backup solution to help prevent loss of transactional data from offices in an earthquake zone. This strategy demonstrates risk:
Which of the following BEST indicates that an organizations risk management program is effective?
Which of the following roles is PRIMARILY accountable for risk associated with business information protection?
Which of the following MUST be assessed before considering risk treatment options for a scenario with significant impact?
Which of the following is MOST important for an organization to update following a change in legislation requiring notification to individuals impacted by data breaches?
A risk practitioner is preparing a report to communicate changes in the risk and control environment. The BEST way to engage stakeholder attention is to:
An organization has an approved bring your own device (BYOD) policy. Which of the following would BEST mitigate the security risk associated with the inappropriate use of enterprise applications on the devices?
An organization is analyzing the risk of shadow IT usage. Which of the following is the MOST important input into the assessment?
Which of the following is the PRIMARY benefit of implementing key control indicators (KCIs)?
What would be the MAIN concern associated with a decentralized IT function maintaining multiple risk registers?
Which of the following should be the GREATEST concern to a risk practitioner when process documentation is incomplete?
A risk practitioner learns of an urgent threat intelligence alert to patch a critical vulnerability identified in the organization's operating system. Which of the following should the risk practitioner do FIRST?
Which of the following is the GREATEST benefit of identifying appropriate risk owners?
In response to the threat of ransomware, an organization has implemented cybersecurity awareness activities. The risk practitioner's BEST recommendation to further reduce the impact of ransomware attacks would be to implement:
A risk practitioner is developing a set of bottom-up IT risk scenarios. The MOST important time to involve business stakeholders is when:
Senior leadership has set guidelines for the integration of a new acquisition. The guidelines allow for a variation in the level of risk-taking. The variation indicates which of the following risk management concepts?
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration for a risk practitioner when making a system implementation go-live recommendation?
The BEST metric to demonstrate that servers are configured securely is the total number of servers:
Which of the following would be MOST helpful when communicating roles associated with the IT risk management process?
An organization has opened a subsidiary in a foreign country. Which of the following would be the BEST way to measure the effectiveness of the subsidiary's IT systems controls?
Which of the following BEST protects an organization against breaches when using a software as a service (SaaS) application?
Which of the following is the BEST way to validate whether controls to reduce user device vulnerabilities have been implemented according to management's action plan?
An organization plans to implement a new Software as a Service (SaaS) speech-to-text solution Which of the following is MOST important to mitigate risk associated with data privacy?
Which of the following should be the PRIMARY area of focus when reporting changes to an organization's risk profile to executive management?
Which of the following helps ensure compliance with a nonrepudiation policy requirement for electronic transactions?
Which of the following is the MOST important reason to communicate risk assessments to senior management?
An organization has implemented a preventive control to lock user accounts after three unsuccessful login attempts. This practice has been proven to be unproductive, and a change in the control threshold value has been recommended. Who should authorize changing this threshold?
Which of the following observations would be the GREATEST concern to a risk practitioner evaluating an organization's risk management practices?
A newly incorporated enterprise needs to secure its information assets From a governance perspective which of the following should be done FIRST?
What would be a risk practitioner's BEST recommendation when several key performance indicators (KPIs) for a control process fail to meet service level agreements (SLAs)?
Which key performance indicator (KPI) BEST measures the effectiveness of an organization's disaster recovery program?
After the announcement of a new IT regulatory requirement, it is MOST important for a risk practitioner to;
An organization has decided to postpone the assessment and treatment of several risk scenarios because stakeholders are unavailable. As a result of this decision, the risk associated with these new entries has been;
An organizational policy requires critical security patches to be deployed in production within three weeks of patch availability. Which of the following is the BEST metric to verify adherence to the policy?
Employees are repeatedly seen holding the door open for others, so that trailing employees do not have to stop and swipe their own ID badges. This behavior BEST represents:
Which of the following is the MOST likely reason an organization would engage an independent reviewer to assess its IT risk management program?
Which of the following will BEST help an organization select a recovery strategy for critical systems?
An IT license audit has revealed that there are several unlicensed copies of co be to:
Which of the following would BEST help to ensure that identified risk is efficiently managed?
Which of the following should be the PRIMARY basis for prioritizing risk responses?
A bank has outsourced its statement printing function to an external service provider. Which of the following is the MOST critical requirement to include in the contract?
An organization uses a web application hosted by a cloud service that is populated by data sent to the vendor via email on a monthly basis. Which of the following should be the FIRST consideration when analyzing the risk associated with the application?
Which of the following BEST assists in justifying an investment in automated controls?
An IT organization is replacing the customer relationship management (CRM) system. Who should own the risk associated with customer data leakage caused by insufficient IT security controls for the new system?
When assessing the maturity level of an organization’s risk management framework, which of the following should be of GREATEST concern to a risk practitioner?
Which of the following should management consider when selecting a risk mitigation option?
When an organization is having new software implemented under contract, which of the following is key to controlling escalating costs?
Which of the following should be the PRIMARY consideration when assessing the automation of control monitoring?
During a post-implementation review for a new system, users voiced concerns about missing functionality. Which of the following is the BEST way for the organization to avoid this situation in the future?
Which of the following BEST prevents control gaps in the Zero Trust model when implementing in the environment?
An organization is increasingly concerned about loss of sensitive data and asks the risk practitioner to assess the current risk level. Which of the following should the risk practitioner do FIRST?
Which of the following should be considered FIRST when creating a comprehensive IT risk register?
From a risk management perspective, which of the following is the PRIMARY purpose of conducting a root cause analysis following an incident?
Which of the following is MOST important for mitigating ethical risk when establishing accountability for control ownership?
Which of the following BEST enables the timely detection of changes in the security control environment?
Which of the following BEST mitigates the risk associated with inadvertent data leakage by users who work remotely?
Which of the following changes would be reflected in an organization's risk profile after the failure of a critical patch implementation?
A bank recently incorporated Blockchain technology with the potential to impact known risk within the organization. Which of the following is the risk practitioner’s BEST course of action?
A risk practitioner is concerned with potential data loss in the event of a breach at a hosted third-party provider. Which of the following is the BEST way to mitigate this risk?
Which of the following is the PRIMARY purpose of creating and documenting control procedures?
Which of the following has the GREATEST impact on backup policies for a system supporting a critical process?
Using key risk indicators (KRIs) to illustrate changes in the risk profile PRIMARILY helps to:
Which of the following is the BEST approach to use when creating a comprehensive set of IT risk scenarios?
Which of the following should be the GREATEST concern for an organization that uses open source software applications?
A risk practitioner is collaborating with key stakeholders to prioritize a large number of IT risk scenarios. Which scenarios should receive the PRIMARY focus?
Which of the following is MOST important to review when determining whether a potential IT service provider’s control environment is effective?
Which of the following should be of GREATEST concern when reviewing the results of an independent control assessment to determine the effectiveness of a vendor's control environment?
Which of the following resources is MOST helpful to a risk practitioner when updating the likelihood rating in the risk register?
Which of the following is the BEST recommendation to senior management when the results of a risk and control assessment indicate a risk scenario can only be partially mitigated?
Which of the following provides The MOST useful information when determining a risk management program's maturity level?
Which of the following is the BEST way for a risk practitioner to verify that management has addressed control issues identified during a previous external audit?
Which of the following observations from a third-party service provider review would be of GREATEST concern to a risk practitioner?
An organization has completed a project to implement encryption on all databases that host customer data. Which of the following elements of the risk register should be updated the reflect this change?
An organization delegates its data processing to the internal IT team to manage information through its applications. Which of the following is the role of the internal IT team in this situation?
Which of the following BEST describes the role of the IT risk profile in strategic IT-related decisions?
Which of the following is a risk practitioner's MOST important course of action when the level of risk has exceeded risk tolerance?
A new software package that could help mitigate risk in an organization has become available. Which of the following is the risk practitioner's BEST course of action?
Key control indicators (KCls) help to assess the effectiveness of the internal control environment PRIMARILY by:
A risk practitioner observed Vial a high number of pokey exceptions were approved by senior management. Which of the following is the risk practitioner’s BEST course of action to determine root cause?
The following is the snapshot of a recently approved IT risk register maintained by an organization's information security department.
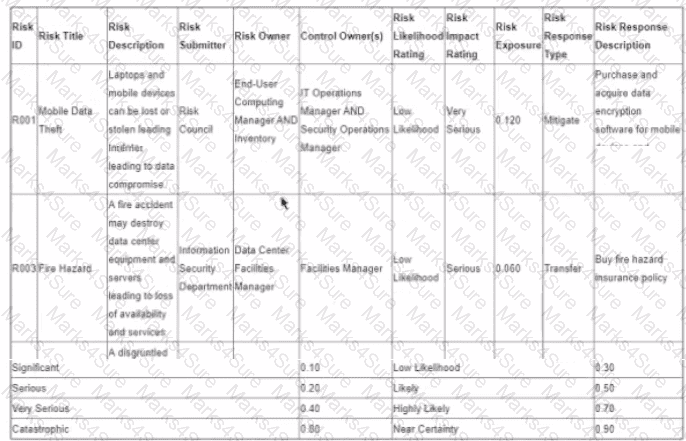
After implementing countermeasures listed in ‘’Risk Response Descriptions’’ for each of the Risk IDs, which of the following component of the register MUST change?
An organization has used generic risk scenarios to populate its risk register. Which of the following presents the GREATEST challenge to assigning of the associated risk entries?
An IT risk practitioner has determined that mitigation activities differ from an approved risk action plan. Which of the following is the risk practitioner's BEST course of action?
After entering a large number of low-risk scenarios into the risk register, it is MOST important for the risk practitioner to:
Which of the following would be the BEST senior management action to influence a strong risk-aware culture within an organization?
Before implementing instant messaging within an organization using a public solution, which of the following should be in place to mitigate data leakage risk?
An IT risk practitioner is evaluating an organization's change management controls over the last six months. The GREATEST concern would be an increase in:
Several network user accounts were recently created without the required management approvals. Which of the following would be the risk practitioner's BEST recommendation to address this situation?
Which of the following would BEST help an enterprise prioritize risk scenarios?
Which of the following would be MOST helpful to an information security management team when allocating resources to mitigate exposures?
Which of the following BEST reduces the risk associated with the theft of a laptop containing sensitive information?
Which of the following is MOST effective in continuous risk management process improvement?
Which of the following is MOST important for an organization to have in place to identify unauthorized devices on the network?
An organization has identified the need to implement an asset tiering model to establish the appropriate level of impact. Which of the following is the MOST effective risk assessment methodology for a risk practitioner to use for this initiative?
After undertaking a risk assessment of a production system, the MOST appropriate action is fcr the risk manager to
Which of the following factors will have the GREATEST impact on the implementation of a risk mitigation strategy for an organization?
Which of the following provides the BEST indication that existing controls are effective?
What are the MOST essential attributes of an effective Key control indicator (KCI)?
Which of the following is the GREATEST concern associated with redundant data in an organization's inventory system?
Which of the following is MOST important for developing effective key risk indicators (KRIs)?
Which of the following is MOST important to understand when determining an appropriate risk assessment approach?
Which of the following should be management's PRIMARY focus when key risk indicators (KRIs) begin to rapidly approach defined thresholds?
Reviewing which of the following would provide the MOST useful information when preparing to evaluate the effectiveness of existing controls?
Reviewing which of the following BEST helps an organization gain insight into its overall risk profile?
What is the BEST recommendation to reduce the risk associated with potential system compromise when a vendor stops releasing security patches and updates for a business-critical legacy system?
Which of the following is MOST helpful in defining an early-warning threshold associated with insufficient network bandwidth’’?
When reporting risk assessment results to senior management, which of the following is MOST important to include to enable risk-based decision making?
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason for a risk practitioner to review an organization's IT asset inventory?
A risk action plan has been changed during the risk mitigation effort. Which of the following is MOST important for the risk practitioner to verify?
An organization has asked an IT risk practitioner to conduct an operational risk assessment on an initiative to outsource the organization's customer service operations overseas. Which of the following would MOST significantly impact management's decision?
An organization recently implemented an automated interface for uploading payment files to its banking system to replace manual processing. Which of the following elements of the risk register is MOST appropriate for the risk practitioner to update to reflect the improved control?
An organization operates in an environment where the impact of ransomware attacks is high, with a low likelihood. After quantifying the impact of the risk associated with ransomware attacks exceeds the organization's risk appetite and tolerance, which of the following is the risk practitioner's BEST recommendation?
During an IT risk scenario review session, business executives question why they have been assigned ownership of IT-related risk scenarios. They feel IT risk is technical in nature and therefore should be owned by IT. Which of the following is the BEST way for the risk practitioner to address these concerns?
Which of the following is the MOST important objective of an enterprise risk management (ERM) program?
Print jobs containing confidential information are sent to a shared network printer located in a secure room. Which of the following is the BEST control to prevent the inappropriate disclosure of confidential information?
An organization recently received an independent security audit report of its cloud service provider that indicates significant control weaknesses. What should be done NEXT in response to this report?
Which of the following is the BEST approach to mitigate the risk associated with a control deficiency?
Which of the following is the PRIMARY risk management responsibility of the third line of defense?
Which of the following is MOST important requirement to include in a Software as a Service (SaaS) vendor contract to ensure data is protected?
A global organization has implemented an application that does not address all privacy requirements across multiple jurisdictions. Which of the following risk responses has the organization adopted with regard to privacy requirements?
What is a risk practitioner's BEST approach to monitor and measure how quickly an exposure to a specific risk can affect the organization?
Which of The following BEST represents the desired risk posture for an organization?
It is MOST important to the effectiveness of an IT risk management function that the associated processes are:
Which of the following is the MOST important driver of an effective enterprise risk management (ERM) program?
Within the three lines of defense model, the responsibility for managing risk and controls resides with:
Which of the following should be the PRIMARY input to determine risk tolerance?
when developing IT risk scenarios associated with a new line of business, which of the following would be MOST helpful to review?
Which of the following is the GREATEST benefit for an organization with a strong risk awareness culture?
A service organization is preparing to adopt an IT control framework to comply with the contractual requirements of a new client. Which of the following would be MOST helpful to the risk practitioner?
When determining which control deficiencies are most significant, which of the following would provide the MOST useful information?
Which of the following BEST contributes to the implementation of an effective risk response action plan?
Which of the following would BEST facilitate the implementation of data classification requirements?
Which of the following should be an element of the risk appetite of an organization?
Which of the following is the BEST approach for performing a business impact analysis (BIA) of a supply-chain management application?
Which of the following is MOST likely to cause a key risk indicator (KRI) to exceed thresholds?
When reviewing the business continuity plan (BCP) of an online sales order system, a risk practitioner notices that the recovery time objective (RTO) has a shorter lime than what is defined in the disaster recovery plan (DRP). Which of the following is the BEST way for the risk practitioner to address this concern?
A risk practitioner has been asked to evaluate a new cloud-based service to enhance an organization's access management capabilities. When is the BEST time for the risk practitioner to provide opinions on control strength?
Numerous media reports indicate a recently discovered technical vulnerability is being actively exploited. Which of the following would be the BEST response to this scenario?
Which of the following is the PRIMARY objective of aggregating the impact of IT risk scenarios and reflecting the results in the enterprise risk register?
An organization has outsourced its IT security operations to a third party. Who is ULTIMATELY accountable for the risk associated with the outsourced operations?
A risk assessment has identified that departments have installed their own WiFi access points on the enterprise network. Which of the following would be MOST important to include in a report to senior management?
Which of the following is the MAIN benefit of involving stakeholders in the selection of key risk indicators (KRIs)?
The MOST important reason to monitor key risk indicators (KRIs) is to help management:
An organization has operations in a location that regularly experiences severe weather events. Which of the following would BEST help to mitigate the risk to operations?
Which of the following is a responsibility of the second line of defense in the three lines of defense model?
If concurrent update transactions to an account are not processed properly, which of the following will MOST likely be affected?
Which of the following BEST indicates the condition of a risk management program?
An organization has initiated a project to implement an IT risk management program for the first time. The BEST time for the risk practitioner to start populating the risk register is when:
To reduce costs, an organization is combining the second and third tines of defense in a new department that reports to a recently appointed C-level executive. Which of the following is the GREATEST concern with this situation?
An enterprise has taken delivery of software patches that address vulnerabilities in its core business software. Prior to implementation, which of the following is the MOST important task to be performed?
Which of the following is the GREATEST concern related to the monitoring of key risk indicators (KRIs)?
Which of the following is MOST important to compare against the corporate risk profile?
When a risk practitioner is building a key risk indicator (KRI) from aggregated data, it is CRITICAL that the data is derived from:
The risk associated with an asset after controls are applied can be expressed as:
An organization's risk profile indicates that residual risk levels have fallen significantly below management's risk appetite. Which of the following is the BEST course of action?
The number of tickets to rework application code has significantly exceeded the established threshold. Which of the following would be the risk practitioner s BEST recommendation?
Which of the following is the GREATEST advantage of implementing a risk management program?
Which of the following is MOST influential when management makes risk response decisions?
To reduce the risk introduced when conducting penetration tests, the BEST mitigating control would be to:
An organization wants to transfer risk by purchasing cyber insurance. Which of the following would be MOST important for the risk practitioner to communicate to senior management for contract negotiation purposes?
When developing a new risk register, a risk practitioner should focus on which of the following risk management activities?
Which of the following provides the MOST reliable evidence of a control's effectiveness?
Which of the following is of GREATEST concern when uncontrolled changes are made to the control environment?
Which of the following is the MOST important criteria for selecting key risk indicators (KRIs)?
Which of the following would be the BEST key performance indicator (KPI) for monitoring the effectiveness of the IT asset management process?
Which of the following conditions presents the GREATEST risk to an application?
Which of the following would BEST facilitate the implementation of data classification requirements?
Which of the following is MOST important for effective communication of a risk profile to relevant stakeholders?
An incentive program is MOST likely implemented to manage the risk associated with loss of which organizational asset?
When reviewing management's IT control self-assessments, a risk practitioner noted an ineffective control that links to several low residual risk scenarios. What should be the NEXT course of action?
As pan of business continuity planning, which of the following is MOST important to include m a business impact analysis (BlA)?
Which of the following would BEST indicate to senior management that IT processes are improving?
A penetration test reveals several vulnerabilities in a web-facing application. Which of the following should be the FIRST step in selecting a risk response?
Which of the following BEST provides an early warning that network access of terminated employees is not being revoked in accordance with the service level agreement (SLA)?
Which of the following contributes MOST to the effective implementation of risk responses?
Which of the following, who should be PRIMARILY responsible for performing user entitlement reviews?
An organization recently implemented new technologies that enable the use of robotic process automation. Which of the following is MOST important to reassess?
A risk practitioner is performing a risk assessment of recent external advancements in quantum computing. Which of the following would pose the GREATEST concern for the risk practitioner?
A risk assessment has identified increased losses associated with an IT risk scenario. It is MOST important for the risk practitioner to:
Of the following, who is responsible for approval when a change in an application system is ready for release to production?
Which of the following is the BEST method to ensure a terminated employee's access to IT systems is revoked upon departure from the organization?
Which of the following would provide the MOST helpful input to develop risk scenarios associated with hosting an organization's key IT applications in a cloud environment?
A highly regulated organization acquired a medical technology startup company that processes sensitive personal information with weak data protection controls. Which of the following is the BEST way for the acquiring company to reduce its risk while still enabling the flexibility needed by the startup company?
Which of the following is MOST important to the effectiveness of a senior oversight committee for risk monitoring?
Which of the following BEST facilitates the mitigation of identified gaps between current and desired risk environment states?
Which of the following is the PRIMARY purpose of periodically reviewing an organization's risk profile?
A business unit has implemented robotic process automation (RPA) for its
repetitive back-office tasks. Which of the following should be the risk
practitioner's GREATEST concern?
Which of the following is MOST helpful in providing a high-level overview of current IT risk severity*?
An organization striving to be on the leading edge in regard to risk monitoring would MOST likely implement:
Which of the following is the MAIN benefit to an organization using key risk indicators (KRIs)?
A peer review of a risk assessment finds that a relevant threat community was not included. Mitigation of the risk will require substantial changes to a software application. Which of the following is the BEST course of action?
An organization plans to migrate sensitive information to a public cloud infrastructure. Which of the following is the GREATEST security risk in this scenario?
Which of the following is the BEST success criterion for control implementation?
Which of the following provides the MOST insight into an organization's IT threat exposure?
Which of the following will BEST ensure that information security risk factors are mitigated when developing in-house applications?
Which of the following would be the GREATEST concern related to data privacy when implementing an Internet of Things (loT) solution that collects personally identifiable information (Pll)?
An organization has outsourced a critical process involving highly regulated data to a third party with servers located in a foreign country. Who is accountable for the confidentiality of this data?
Management has required information security awareness training to reduce the risk associated with credential compromise. What is the BEST way to assess the effectiveness of the training?
Which of the following is the GREATEST concern if user acceptance testing (UAT) is not conducted when implementing a new application?
To ensure key risk indicators (KRIs) are effective and meaningful, the KRIs should be aligned to:
Which of the following is MOST important for a risk practitioner to consider when analyzing the risk associated with migrating to a new cloud service provider?
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration when communicating the risk associated with technology end-of-life to business owners?
An organization is participating in an industry benchmarking study that involves providing customer transaction records for analysis Which of the following is the MOST important control to ensure the privacy of customer information?
Business management is seeking assurance from the CIO that IT has a plan in place for early identification of potential issues that could impact the delivery of a new application Which of the following is the BEST way to increase the chances of a successful delivery'?
A chief information officer (CIO) has identified risk associated with shadow systems being maintained by business units to address specific functionality gaps in the organization'senterprise resource planning (ERP) system. What is the BEST way to reduce this risk going forward?
What should a risk practitioner do FIRST when a shadow IT application is identified in a business owner's business impact analysis (BIA)?
Which of the following is MOST important to the effective monitoring of key risk indicators (KRIS)?
It is MOST important that security controls for a new system be documented in:
Which of the following is the BEST key performance indicator (KPI) to measure the effectiveness of a disaster recovery test of critical business processes?
Which of the following activities is PRIMARILY the responsibility of senior management?
Malware has recently affected an organization. The MOST effective way to resolve this situation and define a comprehensive risk treatment plan would be to perform:
Which of the following will provide the BEST measure of compliance with IT policies?
The BEST way to determine the likelihood of a system availability risk scenario is by assessing the:
Which of the following is the GREATEST concern associated with the lack of proper control monitoring?
Which of the following is MOST helpful in verifying that the implementation of a risk mitigation control has been completed as intended?
Which of the following is a risk practitioner's BEST recommendation to address an organization's need to secure multiple systems with limited IT resources?
Which of the following is the MOST useful indicator to measure the efficiency of an identity and access management process?
Which of the following should a risk practitioner review FIRST when evaluating risk events associated with the organization's data flow model?
Which of the following risk register updates is MOST important for senior management to review?
Which of the following is the BEST way to address a board's concern about the organization's current cybersecurity posture?
A risk practitioner is developing a set of bottom-up IT risk scenarios. The MOST important time to involve business stakeholders is when:
Which of the following is MOST important for a risk practitioner to consider when evaluating plans for changes to IT services?
Which of the following is a PRIMARY benefit to an organization that is using threat intelligence?
Which of the following is the ULTIMATE objective of utilizing key control indicators (KCIs) in the risk management process?
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration when identifying stakeholders to review risk scenarios developed by a risk analyst? The reviewers are:
Zero Trust architecture is designed and deployed with adherence to which of the following basic tenets?
An organization has restructured its business processes, and the business continuity plan (BCP) needs to be revised accordingly. Which of the following should be identified FIRST?
Which of the following BEST supports the management of identified risk scenarios?
Which group has PRIMARY ownership of reputational risk stemming from unethical behavior within the organization?
Which of the following is the PRIMARY purpose for ensuring senior management understands the organization’s risk universe in relation to the IT risk management program?
Which of the following is the MOST effective control to maintain the integrity of system configuration files?
A risk register BEST facilitates which of the following risk management functions?
Which of the following would MOST likely result in updates to an IT risk appetite statement?
Which of the following is the BEST way to address IT regulatory compliance risk?
Which of the following tools is MOST effective in identifying trends in the IT risk profile?
Which of the following BEST represents a critical threshold value for a key control indicator (KCI)?
Which of the following is the BEST key performance indicator (KPI) to measure the effectiveness of a vulnerability management process?
Which of the following will BEST help ensure that risk factors identified during an information systems review are addressed?
What would be MOST helpful to ensuring the effective implementation of a new cybersecurity program?
During the internal review of an accounts payable process, a risk practitioner determines that the transaction approval limits configured in the system are not being enforced. Which of the following should be done NEXT?
Which of the following should be done FIRST when a new risk scenario has been identified
A root because analysis indicates a major service disruption due to a lack of competency of newly hired IT system administrators Who should be accountable for resolving the situation?
Which of the following is the BEST way to mitigate the risk to IT infrastructure availability?
Which of the following will be the GREATEST concern when assessing the risk profile of an organization?
Which of the following is MOST helpful in identifying loss magnitude during risk analysis of a new system?
A risk practitioner discovers that an IT operations team manager bypassed web filtering controls by using a mobile device, in violation of the network security policy. Which of the following should the risk practitioner do FIRST?
An organization wants to launch a campaign to advertise a new product Using data analytics, the campaign can be targeted to reach potential customers. Which of the following should be of GREATEST concern to the risk practitioner?
Which of the following is the BEST indication that key risk indicators (KRIs) should be revised?
Which of the following attributes of a key risk indicator (KRI) is MOST important?
An organization has implemented immutable backups to prevent successful ransomware attacks. Which of the following is the MOST effective control for the risk practitioner to review?
Which of the following is the BEST method to mitigate the risk of an unauthorized employee viewing confidential data in a database''
A key risk indicator (KRI) that incorporates data from external open-source threat intelligence sources has shown changes in risk trend data. Which of the following is MOST important to update in the risk register?
Which of the following MOST effectively limits the impact of a ransomware attack?
The software version of an enterprise's critical business application has reached end-of-life and is no longer supported by the vendor. IT has decided to develop an in-house replacement application. Which of the following should be the PRIMARY concern?
Which of the following is MOST important to understand when developing key risk indicators (KRIs)?
Which of the following would be MOST helpful when estimating the likelihood of negative events?
During a risk treatment plan review, a risk practitioner finds the approved risk action plan has not been completed However, there were other risk mitigation actions implemented. Which of the fallowing is the BEST course of action?
Which of the following would MOST likely drive the need to review and update key performance indicators (KPIs) for critical IT assets?
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason to use key control indicators (KCIs) to evaluate control operating effectiveness?
Which of the following would be the GREATEST risk associated with a new implementation of single sign-on?
While conducting an organization-wide risk assessment, it is noted that many of the information security policies have not changed in the past three years. The BEST course of action is to:
Which of the following will BEST help mitigate the risk associated with malicious functionality in outsourced application development?
Which of the following should be the PRIMARY goal of developing information security metrics?
What should be the PRIMARY consideration related to data privacy protection when there are plans for a business initiative to make use of personal information?
A risk practitioner has just learned about new malware that has severely impacted industry peers worldwide data loss?
Which of the following risk management practices BEST facilitates the incorporation of IT risk scenarios into the enterprise-wide risk register?
Which of the following would MOST likely cause a risk practitioner to reassess risk scenarios?
Which of the following is the MOST important benefit of implementing a data classification program?
Which of the following is the PRIMARY advantage of having a single integrated business continuity plan (BCP) rather than each business unit developing its own BCP?
An IT department has provided a shared drive for personnel to store information to which all employees have access. Which of the following parties is accountable for the risk of potential loss of confidential information?
Which of the following should be a risk practitioner's GREATEST concern upon learning of failures in a data migration activity?
Which of the following would be MOST useful to management when allocating resources to mitigate risk to the organization?
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration for protecting data assets m a Business application system?
When of the following 15 MOST important when developing a business case for a proposed security investment?
Which of the following provides the BEST evidence that robust risk management practices are in place within an organization?
Which of the following would be MOST relevant to stakeholders regarding ineffective control implementation?
Which of the following is the MOST important reason for a risk practitioner to identify stakeholders for each IT risk scenario?
The BEST key performance indicator (KPI) to measure the effectiveness of a vulnerability remediation program is the number of:
Which of the following is the GREATEST concern when establishing key risk indicators (KRIs)?
Which of the following should a risk practitioner recommend be done prior to disposal of server hardware containing confidential data?
A risk practitioner is reviewing the status of an action plan to mitigate an emerging IT risk and finds the risk level has increased. The BEST course of action would be to:
Whether the results of risk analyses should be presented in quantitative or qualitative terms should be based PRIMARILY on the:
Which of the following describes the relationship between risk appetite and risk tolerance?
Which of the following should be done FIRST upon learning that the organization will be affected by a new regulation in its industry?
A risk practitioner identifies a database application that has been developed and implemented by the business independently of IT. Which of the following is the BEST course of action?
It was discovered that a service provider's administrator was accessing sensitive information without the approval of the customer in an Infrastructure as a Service (laaS) model. Which of the following would BEST protect against a future recurrence?
After an annual risk assessment is completed, which of the following would be MOST important to communicate to stakeholders?
Which of the following provides the BEST evidence of the effectiveness of an organization's account provisioning process?
Which of the following actions should a risk practitioner do NEXT when an increased industry trend of external cyber attacks is identified?
Which of the following is the MOST effective way to help ensure future risk levels do not exceed the organization's risk appetite?
Which of the following should be the risk practitioner's FIRST course of action when an organization plans to adopt a cloud computing strategy?
Which of the following is the MOST important factor when deciding on a control to mitigate risk exposure?
Senior management is deciding whether to share confidential data with the organization's business partners. The BEST course of action for a risk practitioner would be to submit a report to senior management containing the:
An organization's chief information officer (CIO) has proposed investing in a new. untested technology to take advantage of being first to market Senior management has concerns about the success of the project and has set a limit for expenditures before final approval. This conditional approval indicates the organization's risk:
A vendor's planned maintenance schedule will cause a critical application to temporarily lose failover capabilities. Of the following, who should approve this proposed schedule?
Which of the following is MOST important for senior management to review during an acquisition?
Reviewing which of the following provides the BEST indication of an organizations risk tolerance?
Who is PRIMARILY accountable for identifying risk on a daily basis and ensuring adherence to the organization's policies?
A risk practitioner discovers several key documents detailing the design of a product currently in development have been posted on the Internet. What should be the risk practitioner's FIRST course of action?
Which of the following presents the GREATEST concern associated with the
use of artificial intelligence (Al) systems?
When developing risk scenario using a list of generic scenarios based on industry best practices, it is MOST imported to:
In addition to the risk register, what should a risk practitioner review to develop an understanding of the organization's risk profile?
Which of the following facilitates a completely independent review of test results for evaluating control effectiveness?
What is the MAIN benefit of using a top-down approach to develop risk scenarios?
Which of the following will BEST help to ensure that information system controls are effective?
A business manager wants to leverage an existing approved vendor solution from another area within the organization. Which of the following is the risk practitioner's BEST course of action?
An organization has been experiencing an increasing number of spear phishing attacks Which of the following would be the MOST effective way to mitigate the risk associated with these attacks?
Which of the following should be a risk practitioner's PRIMARY focus when tasked with ensuring organization records are being retained for a sufficient period of time to meet legal obligations?
Which of the following provides the BEST protection for Internet of Things (loT) devices that are accessed within an organization?
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason for a risk practitioner to use global standards related to risk management?
Which of the following would provide executive management with the BEST information to make risk decisions as a result of a risk assessment?
Which of the following is the BEST control for a large organization to implement to effectively mitigate risk related to fraudulent transactions?
Upon learning that the number of failed back-up attempts continually exceeds the current risk threshold, the risk practitioner should:
A penetration testing team discovered an ineffectively designed access control. Who is responsible for ensuring the control design gap is remediated?
Which of the following emerging technologies is frequently used for botnet distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks?
Which of the following is the MOST effective way to reduce potential losses due to ongoing expense fraud?
A risk practitioner notices that a particular key risk indicator (KRI) has remained below its established trigger point for an extended period of time. Which of the following should be done FIRST?
A new international data privacy regulation requires personal data to be
disposed after the specified retention period, which is different from the local
regulatory requirement. Which of the following is the risk practitioner's
BEST course of action?
It is MOST important for a risk practitioner to have an awareness of an organization s processes in order to:
Which of the following is the PRIMARY role of the first line of defense with respect to information security policies?
A risk practitioner has been asked to assess the risk associated with a new critical application used by a financial process team that the risk practitioner was a member of two years ago. Which of the following is the GREATEST concern with this request?
Key risk indicators (KRIs) are MOST useful during which of the following risk management phases?
Which of the following is the PRIMARY advantage of aligning generic risk scenarios with business objectives?
Which of the following should a risk practitioner recommend FIRST when an increasing trend of risk events and subsequent losses has been identified?
An organization has agreed to a 99% availability for its online services and will not accept availability that falls below 98.5%. This is an example of:
Several newly identified risk scenarios are being integrated into an organization's risk register. The MOST appropriate risk owner would be the individual who:
A risk practitioner recently discovered that personal information from the production environment is required for testing purposes in non-production environments. Which of the following is the BEST recommendation to address this situation?
Which of the following is the MOST important data attribute of key risk indicators (KRIs)?
An organization is planning to acquire a new financial system. Which of the following stakeholders would provide the MOST relevant information for analyzing the risk associated with the new IT solution?
Which of the following BEST reduces the likelihood of employees unintentionally disclosing sensitive information to outside parties?
Which of the following approaches MOST effectively enables accountability for data protection?
Which of the following BEST enables a risk practitioner to identify the consequences of losing critical resources due to a disaster?
Which of the following is the BEST key performance indicator (KPI) to measure the effectiveness of a disaster recovery plan (DRP)?
Which of the following BEST facilitates the identification of appropriate key performance indicators (KPIs) for a risk management program?
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason to establish the root cause of an IT security incident?
An organization learns of a new ransomware attack affecting organizations worldwide. Which of the following should be done FIRST to reduce the likelihood of infection from the attack?
The implementation of a risk treatment plan will exceed the resources originally allocated for the risk response. Which of the following should be the risk owner's NEXT action?
Which of the following controls BEST enables an organization to ensure a complete and accurate IT asset inventory?
Which of the following trends would cause the GREATEST concern regarding the effectiveness of an organization's user access control processes? An increase in the:
Which of the following is the MOST important technology control to reduce the likelihood of fraudulent payments committed internally?
An organization is measuring the effectiveness of its change management program to reduce the number of unplanned production changes. Which of the following would be the BEST metric to determine if the program is performing as expected?
Which of the following provides the MOST useful information to assess the magnitude of identified deficiencies in the IT control environment?
Improvements in the design and implementation of a control will MOST likely result in an update to:
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason to update a risk register with risk assessment results?
Which of the following provides the BEST assurance of the effectiveness of vendor security controls?
Which of the following BEST supports the communication of risk assessment results to stakeholders?
Within the three lines of defense model, the accountability for the system of internal control resides with:
Which of the following is MOST helpful to facilitate the decision of recovery priorities in a disaster situation?
Which of the following should be accountable for ensuring that media containing financial information are adequately destroyed per an organization's data disposal policy?
A risk manager has determined there is excessive risk with a particular technology. Who is the BEST person to own the unmitigated risk of the technology?
Which of the following would be a risk practitioner's GREATEST concern with the use of a vulnerability scanning tool?
An unauthorized individual has socially engineered entry into an organization's secured physical premises. Which of the following is the BEST way to prevent future occurrences?
All business units within an organization have the same risk response plan for creating local disaster recovery plans. In an effort to achieve cost effectiveness, the BEST course of action would be to:
A failure in an organization s IT system build process has resulted in several computers on the network missing the corporate endpoint detection and response (EDR) software. Which of the following should be the risk practitioner’s IMMEDIATE concern?
Which of the following should an organization perform to forecast the effects of a disaster?
During a routine check, a system administrator identifies unusual activity indicating an intruder within a firewall. Which of the following controls has MOST likely been compromised?
Which of the following is the BEST way to determine the value of information assets for risk management purposes?
Which of the following criteria associated with key risk indicators (KRIs) BEST enables effective risk monitoring?
A bank is experiencing an increasing incidence of customer identity theft. Which of the following is the BEST way to mitigate this risk?
Which of the following is a risk practitioner's BEST recommendation to help reduce IT risk associated with scheduling overruns when starting a new application development project?
Management has determined that it will take significant time to remediate exposures in the current IT control environment. Which of the following is the BEST course of action?
Controls should be defined during the design phase of system development because:
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration when selecting either a qualitative or quantitative risk analysis?
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration when multiple risk practitioners capture risk scenarios in a single risk register?
Which of the following BEST indicates the effective implementation of a risk treatment plan?
Which of the following is the MOST important risk management activity during project initiation?
Which of the following would present the GREATEST challenge when assigning accountability for control ownership?
Which of the following is the ULTIMATE goal of conducting a privacy impact analysis (PIA)?
What is the MOST important consideration when aligning IT risk management with the enterprise risk management (ERM) framework?
A risk practitioner is asked to present the results of the most recent technology risk assessment to executive management in a concise manner. Which of the following is MOST important to include in the presentation?
Who is accountable for authorizing application access in a cloud Software as a Service (SaaS) solution?
An organization is considering the adoption of an aggressive business strategy to achieve desired growth From a risk management perspective what should the risk practitioner do NEXT?
Which of the following is the PRIMARY factor in determining a recovery time objective (RTO)?
Implementing which of the following controls would BEST reduce the impact of a vulnerability that has been exploited?
Which of the following is the MOST important consideration when selecting key risk indicators (KRIs) to monitor risk trends over time?
A hospital recently implemented a new technology to allow virtual patient appointments. Which of the following should be the risk practitioner's FIRST course of action?
A risk practitioner has observed that there is an increasing trend of users sending sensitive information by email without using encryption. Which of the following would be the MOST effective approach to mitigate the risk associated with data loss?
What should a risk practitioner do FIRST when vulnerability assessment results identify a weakness in an application?
A public online information security training course is available to an organization's staff. The online course contains free-form discussion fields. Which of the following should be of MOST concern to the organization's risk practitioner?
Which of the following provides the MOST important information to facilitate a risk response decision?
Which of the following stakeholders are typically included as part of a line of defense within the three lines of defense model?
Which of the following is a KEY consideration for a risk practitioner to communicate to senior management evaluating the introduction of artificial intelligence (Al) solutions into the organization?
Which of the following provides the BEST evidence that a selected risk treatment plan is effective?
An IT operations team implements disaster recovery controls based on decisions from application owners regarding the level of resiliency needed. Who is the risk owner in this scenario?
An IT risk practitioner has been asked to regularly report on the overall status and effectiveness of the IT risk management program. Which of the following is MOST useful for this purpose?
Which of the following would be a weakness in procedures for controlling the migration of changes to production libraries?
Which of the following methods would BEST contribute to identifying obscure risk scenarios?
Which of the following is MOST important to ensure risk management practices are effective at all levels within the organization?
Which of the following is the BEST approach when a risk practitioner has been asked by a business unit manager for special consideration during a risk assessment of a system?
An organization has determined that risk is not being adequately tracked and
managed due to a distributed operating model. Which of the following is the
BEST way to address this issue?
Which of the following will BEST help to ensure implementation of corrective action plans?
After the review of a risk record, internal audit questioned why the risk was lowered from medium to low. Which of the following is the BEST course of action in responding to this inquiry?
A risk heat map is MOST commonly used as part of an IT risk analysis to facilitate risk:
The PRIMARY reason for establishing various Threshold levels for a set of key risk indicators (KRIs) is to:
Which of the following methods is the BEST way to measure the effectiveness of automated information security controls prior to going live?
A risk practitioner has become aware of production data being used in a test environment. Which of the following should be the practitioner's PRIMARY concern?
Which of the following would BEST help secure online financial transactions from improper users?
Which of the following BEST indicates effective information security incident management?
Before selecting a final risk response option for a given risk scenario, management should FIRST:
Which of the following should be the PRIMARY focus of an independent review of a risk management process?
Which of the following activities should only be performed by the third line of defense?
During a control review, the control owner states that an existing control has deteriorated over time. What is the BEST recommendation to the control owner?
Which of the following is the GREATEST benefit of updating the risk register to include outcomes from a risk assessment?
Which of the following would be MOST useful to senior management when determining an appropriate risk response?
To drive effective risk management, it is MOST important that an organization's policy framework is:
Which of the following information is MOST useful to a risk practitioner for developing IT risk scenarios?
Which of the following is the PRIMARY benefit of consistently recording risk assessment results in the risk register?
Which of the following is the GREATEST concern when using artificial intelligence (AI) language models?
Which of the following is the BEST indicator of the effectiveness of a control action plan's implementation?
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason to have the risk management process reviewed by a third party?
Which of the following risk scenarios would be the GREATEST concern as a result of a single sign-on implementation?
Which of the following BEST enables risk-based decision making in support of a business continuity plan (BCP)?
A risk practitioner has been notified that an employee sent an email in error containing customers' personally identifiable information (Pll). Which of the following is the risk practitioner's BEST course of action?
Which of the following would BEST help to ensure that suspicious network activity is identified?
What is the BEST information to present to business control owners when justifying costs related to controls?
Which of the following is a risk practitioner's MOST appropriate course of action upon learning that an organization is not compliant with its patch management policy?
Which of the following would provide the MOST objective assessment of the effectiveness of an organization's security controls?
Which of the following is the GREATEST benefit of a three lines of defense structure?
Which of the following should be done FIRST when developing an initial set of risk scenarios for an organization?
Which of the following is MOST important when conducting a post-implementation review as part of the system development life cycle (SDLC)?
Which of the following is the MOST effective way for a large and diversified organization to minimize risk associated with unauthorized software on company devices?
After undertaking a risk assessment of a production system, the MOST appropriate action is for the risk manager to:
Which of the following is the MOST important reason to validate that risk responses have been executed as outlined in the risk response plan''
Which of the following should be determined FIRST when a new security vulnerability is made public?
A business is conducting a proof of concept on a vendor's Al technology. Which of the following is the MOST important consideration for managing risk?
Which of the following would be MOST useful when measuring the progress of a risk response action plan?
Which of the following situations would cause the GREATEST concern around the integrity of application logs?
Which of the following indicates an organization follows IT risk management best practice?
The BEST reason to classify IT assets during a risk assessment is to determine the:
Which of the following controls will BEST mitigate risk associated with excessive access privileges?
Which of the following would MOST likely cause management to unknowingly accept excessive risk?
Which of the following would BEST mitigate the ongoing risk associated with operating system (OS) vulnerabilities?
To define the risk management strategy which of the following MUST be set by the board of directors?
An organization has decided to outsource a web application, and customer data will be stored in the vendor's public cloud. To protect customer data, it is MOST important to ensure which of the following?
A financial organization is considering a project to implement the use of blockchain technology. To help ensure the organization's management team can make informed decisions on the project, which of the following should the risk practitioner reassess?
Which of the following is the BEST way to help ensure risk will be managed properly after a business process has been re-engineered?
Which of the following should be the PRIMARY consideration when assessing the risk of using Internet of Things (loT) devices to collect and process personally identifiable information (Pll)?
An organization has established a single enterprise-wide risk register that records high-level risk scenarios. The IT risk department has created its own register to record more granular scenarios applicable to IT. Which of the following is the BEST way to ensure alignment between these two registers?
When confirming whether implemented controls are operating effectively, which of the following is MOST important to review?
Which of the following is a drawback in the use of quantitative risk analysis?
During a risk assessment of a financial institution, a risk practitioner discovers that tellers can initiate and approve transactions of significant value. This team is also responsible for ensuring transactions are recorded and balances are reconciled by the end of the day. Which of the following is the risk practitioner's BEST recommendation to mitigate the associated risk?
Which of the following will BEST help to ensure key risk indicators (KRIs) provide value to risk owners?
Which of the following is the PRIMARY reason to perform ongoing risk assessments?
From a business perspective, which of the following is the MOST important objective of a disaster recovery test?
A global organization is considering the transfer of its customer information systems to an overseas cloud service provider in the event of a disaster. Which of the following should be the MOST important risk consideration?
Which of the following would provide the BEST evidence of an effective internal control environment/?
Vulnerabilities have been detected on an organization's systems. Applications installed on these systems will not operate if the underlying servers are updated. Which of the following is the risk practitioner's BEST course of action?
Which of the following would be the GREATEST concern for an IT risk practitioner when an employees.....
The risk associated with data loss from a website which contains sensitive customer information is BEST owned by:
Which of the following is the GREATEST risk associated with the misclassification of data?
The MOST significant benefit of using a consistent risk ranking methodology across an organization is that it enables:
After several security incidents resulting in significant financial losses, IT management has decided to outsource the security function to a third party that provides 24/7 security operation services. Which risk response option has management implemented?
Who is MOST important lo include in the assessment of existing IT risk scenarios?
An organization wants to assess the maturity of its internal control environment. The FIRST step should be to:
The risk associated with a high-risk vulnerability in an application is owned by the:
Which of the following is the BEST indication of an improved risk-aware culture following the implementation of a security awareness training program for all employees?
Which of the following is MOST important to consider when determining the risk associated with re-identification of obfuscated personal data?