Which of the following best describes why PXE boot endpoints should be exempt from Assessment policies?
Because they will not be subject to the Acceptable Use Policy
They have already been deployed and should immediately be subject to Assessment policies
Because they are not yet manageable and may not have all the required software and services installed
Because they will never be manageable or have the required software and services
Because they are special endpoints playing a specific role in the network
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
PXE (Preboot Execution Environment) boot endpoints should be exempt from Assessment policies because they are not yet manageable and may not have all the required software and services installed. According to the Forescout Administration Guide, endpoints in the early stages of deployment, such as those booting via PXE, are temporary in nature and lack the necessary management capabilities and required software components.
PXE Boot Endpoints Characteristics:
PXE boot endpoints represent machines in a temporary state during the deployment process:
Not Yet Fully Deployed - PXE boot is used during initial OS installation and deployment
Lack Required Services - The endpoint does not yet have installed:
SecureConnector (if required for management)
Endpoint agents
Required security software
Management services
Limited Configuration - The endpoint may not have completed network configuration
Temporary State - PXE boot endpoints are in a transient state, not their final operational state
Policy Endpoint Exceptions:
According to the documentation, administrators can "select endpoints in the Detections pane and exempt them from further inspection for the policy that detected them". This is particularly important for PXE boot endpoints because:
False Positives - Assessment policies might flag PXE boot endpoints as non-compliant due to missing software that hasn't been installed yet
Blocked Deployment - If blocking actions are applied, they could interfere with the deployment process
Temporary Assessment - Once the endpoint is fully deployed and manageable, it can be added back to Assessment policies
Operational Efficiency - Exempting PXE boot endpoints prevents unnecessary policy violations during the deployment window
Manageable vs. Unmanageable Endpoints:
According to the documentation:
"Endpoints are generally unmanageable if their remote registry and file system cannot be accessed by Forescout. Unmanageable hosts can be included in your policy."
PXE boot endpoints specifically fall into this category because:
Remote management is not yet available
Required agents are not installed
File system access is not established
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Because they will not be subject to the Acceptable Use Policy - Not the primary reason; Assessment policies differ from Acceptable Use policies
B. They have already been deployed and should immediately be subject to Assessment policies - Contradicts the purpose; PXE boot endpoints are NOT yet deployed
D. Because they will never be manageable or have the required software and services - Incorrect; once deployed, they WILL become manageable
E. Because they are special endpoints playing a specific role in the network - While true in context, this doesn't explain why they need exemption
Referenced Documentation:
Forescout Administration Guide - Create Policy Endpoint Exceptions
Restricting Endpoint Inspection documentation
Manage Actions - Unmanageable hosts section
Based on ForeScout's recommended troubleshooting approach, where should you start the troubleshooting process?
Run fstool tech-support
Check that requirements are met
Look at dependencies
Examine the GUI Logs
Review command line logs
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Forescout troubleshooting methodology, the recommended starting point for the troubleshooting process is to "Check that requirements are met". This foundational step must come before any detailed investigation.
Forescout Troubleshooting Approach:
The basic troubleshooting workflow consists of:
text
Step 1: CHECK THAT REQUIREMENTS ARE MET (START HERE)
├─ System requirements
├─ Software versions
├─ Network connectivity
└─ Licensing
Step 2: Look at Dependencies
├─ Network dependencies
├─ Service dependencies
└─ Appliance dependencies
Step 3: Gather Information from CounterACT
├─ GUI logs
├─ Properties
└─ Policies
Step 4: Gather Information from Command Line
├─ CLI logs
└─ Network diagnostics
Step 5: Form Hypothesis and Diagnose
├─ Analyze findings
└─ Determine root cause
Why Checking Requirements is the First Step:
According to the troubleshooting best practices:
Foundation - Verifying requirements prevents wasting time on invalid configurations
System Integrity - Ensures all prerequisites are met before investigating issues
Efficiency - Many issues stem from unmet requirements; fixing these resolves the problem immediately
Logical Flow - Without meeting requirements, no further troubleshooting will be effective
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Run fstool tech-support - This is an advanced diagnostic tool, not the starting point
C. Look at dependencies - Dependencies are examined AFTER confirming requirements are met
D. Examine the GUI Logs - Logs are reviewed AFTER requirements and dependencies are checked
E. Review command line logs - CLI logs are examined later in the process, not first
Requirements Verification Includes:
According to the methodology:
System Requirements
Supported OS versions
Memory and storage requirements
CPU specifications
Software Versions
Forescout platform version
Plugin/module compatibility
Browser versions for Console
Network Connectivity
IP address configuration
Network interfaces
Firewall rules
Licensing
Valid licenses
License not expired
License for required modules
Referenced Documentation:
Basic troubleshooting approach methodology
Which field in the User Directory plugin should be configured for Active Directory subdomains?
Replicas
Address
Parent Groups
Domain Aliases
DNS Detection
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Forescout User Directory Plugin Configuration Guide - Microsoft Active Directory Server Settings, the field that should be configured for Active Directory subdomains is "Domain Aliases".
Domain Aliases for Subdomains:
According to the Microsoft Active Directory Server Settings documentation:
"Configure the following additional server settings in the Directory and Additional Domain Aliases sections: Domain Aliases - Configure additional domain names that users can use to log in, such as subdomains."
Purpose of Domain Aliases:
According to the documentation:
Domain Aliases are used to specify:
Subdomains - Alternative domain names like subdomain.company.com
Alternative Domain Names - Other domain name variations
User Login Options - Additional domains users can use to authenticate
Alias Resolution - Maps aliases to the primary domain
Example Configuration:
For an organization with the primary domain company.com and subdomain accounts.company.com:
Domain Field - Set to: company.com
Domain Aliases Field - Add: accounts.company.com
This allows users from either domain to authenticate successfully.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Replicas - Replicas configure redundant User Directory servers, not subdomains
B. Address - Address field specifies the server IP/FQDN, not domain aliases
C. Parent Groups - Parent Groups relate to group hierarchy, not domain subdomains
E. DNS Detection - DNS Detection is not a User Directory configuration field
Additional Domain Configuration:
According to the documentation:
text
Primary Configuration:
├─ Domain: company.com
├─ Domain Aliases: accounts.company.com
│ services.company.com
│ mail.company.com
└─ Port: 636 (default)
Referenced Documentation:
Microsoft Active Directory Server Settings
Define User Directory Servers - Domain Aliases section
When an admission event is seen, how are main rules and sub-rules processed?
Main rules process concurrently, sub-rules process sequentially.
Main rules process in parallel, sub-rules process concurrently.
Main rules process concurrently, sub-rules process in parallel.
Main rules process sequentially, sub-rules process concurrently.
Main rules process sequentially, sub-rules process in parallel.
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Forescout Administration Guide - Policy Processing, when an admission event occurs, "Main rules process concurrently, sub-rules process sequentially".
Policy Processing Flow:
According to the Main Rule Advanced Options documentation:
When an admission event triggers policy evaluation:
Main Rules - Process concurrently/in parallel
All main rules are evaluated simultaneously
No ordering or sequencing
Each main rule evaluates independently
Sub-Rules - Process sequentially/in order
Sub-rules within each main rule execute one after another
First match wins - stops evaluating subsequent sub-rules
Order matters for sub-rule execution
Main Rule Concurrent Processing:
According to the documentation:
"Main rules are evaluated independently and concurrently. Multiple main rules can be processed simultaneously for the same endpoint."
Sub-Rule Sequential Processing:
According to the Defining Policy Sub-Rules documentation:
"Sub-rules are evaluated sequentially in the order defined. When an endpoint matches a sub-rule, that sub-rule's actions are taken and subsequent sub-rules are not evaluated."
Example Processing:
When admission event triggers:
text
CONCURRENT (Main Rules):
├─ Main Rule 1 evaluation → Sub-rule processing (sequential)
├─ Main Rule 2 evaluation → Sub-rule processing (sequential)
└─ Main Rule 3 evaluation → Sub-rule processing (sequential)
(All main rules evaluate at the same time)
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
B. Parallel/Concurrently - "Concurrent" and "parallel" mean the same thing; sub-rules don't process concurrently
C. Concurrent/Parallel - Sub-rules don't process in parallel; they're sequential
D. Sequential/Concurrently - Main rules don't process sequentially; they're concurrent
E. Sequential/Parallel - Main rules don't process sequentially; they're concurrent
Referenced Documentation:
Main Rule Advanced Options
Defining Policy Sub-Rules
Select the action that requires symmetrical traffic.
Assign to VLAN
WLAN block
Endpoint ACL
Start SecureConnector
Virtual Firewall
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Forescout Administration Guide and Switch Plugin documentation, the action that requires symmetrical traffic is the Endpoint Address ACL action (C).
What "Symmetrical Traffic" Means:
Symmetrical traffic refers to network traffic where CounterACT can monitor BOTH directions of communication:
Inbound - Traffic from the endpoint
Outbound - Traffic to the endpoint
This allows CounterACT to see the complete conversation flow.
Endpoint Address ACL Requirements:
According to the Switch Plugin documentation:
"The Endpoint Address ACL action applies an ACL that delivers blocking protection when endpoints connect to the network. Other benefits of Endpoint Address ACL include..."
For the Endpoint Address ACL to function properly, CounterACT must:
See bidirectional traffic - Monitor packets in both directions
Apply dynamic ACLs - Create filtering rules based on both source and destination
Verify endpoints - Ensure the endpoint IP/MAC matches expected patterns in both directions
Why Symmetrical Traffic is Required:
According to the documentation:
Endpoint Address ACLs work by:
Identifying the endpoint's MAC address and IP address through bidirectional observation
Creating switch ACLs that filter based on the endpoint's communication patterns
Verifying the endpoint is communicating in expected ways (symmetrically)
Without symmetrical traffic visibility, CounterACT cannot reliably identify and apply address-based filtering.
Why Other Options Do NOT Require Symmetrical Traffic:
A. Assign to VLAN - Only requires knowing the switch port; doesn't need traffic monitoring
B. WLAN block - Works at the wireless access point level without needing symmetrical traffic observation
D. Start SecureConnector - Deployment action that doesn't require traffic symmetry
E. Virtual Firewall - Works at the endpoint level and can function with asymmetrical or passive monitoring
Asymmetrical vs. Symmetrical Deployment:
According to the administrative guide:
Asymmetrical Deployment - CounterACT sees traffic from one direction only
Used for passive monitoring of device discovery
Sufficient for many actions
Symmetrical Deployment - CounterACT sees traffic in both directions
Required for endpoint ACL actions
Necessary for accurate address-based filtering
Referenced Documentation:
Endpoint Address ACL Action documentation
ForeScout CounterACT Administration Guide - Switch Plugin actions
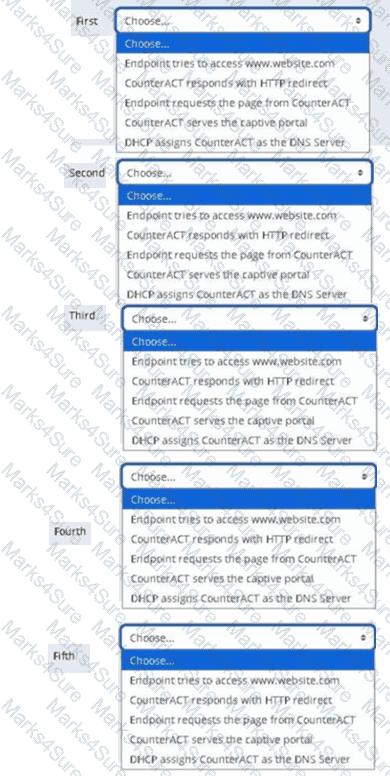
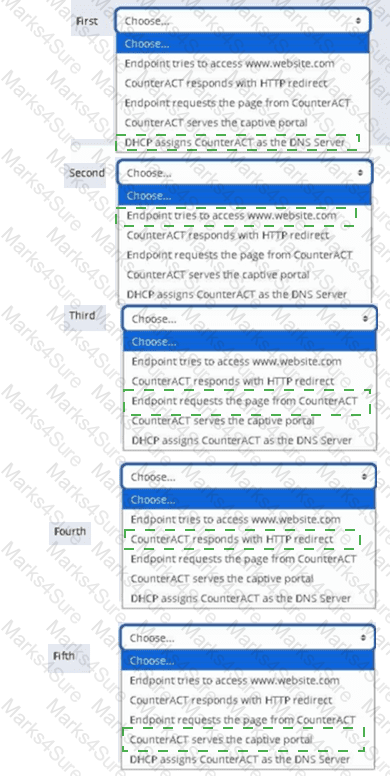
Place the DNS Enforce control actions into the correct workflow order for endpoints which have a pending control action.
What is true of the "Use as directory" selection configured below?

Select one:
It allows resolution of User information via LDAP
It allows resolution of user information via TACACS
It allows for Guest Registration when Approvals are required
It enables HTTP authentication and resolves HTTP login status
It allows resolution of user information via RADIUS
According to the Forescout User Directory Plugin Configuration Guide and the RADIUS Plugin Configuration Guide Version 4.3, the "Use as directory" selection allows resolution of user information via LDAP. The documentation explicitly states:
"Use as directory: Select this option to use the server as a directory to retrieve user information. This option is not available for RADIUS and TACACS servers."
What "Use as directory" Does:
According to the User Directory Plugin documentation:
When "Use as directory" is selected on a User Directory server configuration:
LDAP Query Capability - The server can be queried via LDAP to retrieve user information
User Resolution - User details are resolved by querying the LDAP directory
Directory Lookups - User properties (group membership, attributes, contact info) are retrieved from the directory
Policy Matching - Users can be matched in policies based on directory group membership
Supported Server Types for "Use as directory":
According to the configuration guide:
The "Use as directory" option is available for:
Microsoft Active Directory (via LDAP protocol)
OpenLDAP (via LDAP protocol)
Other LDAP-compatible directory servers
The "Use as directory" option is NOT available for:
RADIUS servers - Cannot be used as a directory
TACACS servers - Cannot be used as a directory
Why RADIUS/TACACS Cannot Be Directories:
According to the documentation:
RADIUS and TACACS are authentication and authorization protocols, NOT directory protocols
They do not support directory-style lookups and user attribute queries
They only provide authentication (username/password verification) and authorization (what the user can do)
They cannot provide the rich user information that LDAP directories can provide
LDAP as a Directory Protocol:
According to the documentation:
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) provides:
User Information Storage - Stores user objects with multiple attributes
Directory Queries - Can query for specific users and their properties
Group Membership - Can retrieve LDAP group information
Attribute Resolution - Can access user attributes for policy conditions
Three Critical Checkboxes:
According to the RADIUS Plugin Configuration Guide:
"Make sure that both the Use as directory option and the Use for authentication option are enabled."
This indicates that a single User Directory server can have multiple roles:
Use as directory - For LDAP queries and user information resolution
Use for authentication - For user login authentication
Use for Console Login - For access to the Forescout Console
Example Configuration:
According to the documentation:
When you have an Active Directory server:
✓ "Use as directory" is CHECKED - Enables LDAP queries for user info and group membership
✓ "Use for authentication" is CHECKED - Allows users to authenticate with their AD credentials
✓ "Use for Console Login" is CHECKED - Allows administrators to log into Forescout Console with AD credentials
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
B. It allows resolution of user information via TACACS - Explicitly NOT available for TACACS; TACACS cannot function as a directory
C. It allows for Guest Registration when Approvals are required - This is a separate User Directory feature unrelated to "Use as directory"
D. It enables HTTP authentication and resolves HTTP login status - This is not related to directory usage; HTTP authentication is a separate feature
E. It allows resolution of user information via RADIUS - Explicitly NOT available for RADIUS; RADIUS servers cannot function as directories
Referenced Documentation:
User Directory Plugin Configuration - Define User Directory Servers
User Directory Plugin - Name and Type Step documentation
RADIUS Plugin Configuration Guide Version 4.3 - User Directory Readiness section
Why is SMB required for Windows Manageability?
Scripts run on CounterACT are copied to a temp directory and run locally on the endpoint
Scripts run on endpoints are copied to a Linux script repository and run locally on the endpoint
Scripts run on endpoints are copied to a temp directory and run remotely from CounterACT
Scripts run on CounterACT are copied to a script repository and run remotely from CounterACT
Scripts run on endpoints are copied to a temp directory and run locally on the endpoint
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Forescout CounterACT HPS Inspection Engine Configuration Guide Version 10.8, SMB (Server Message Block) is required for Windows Manageability because scripts run on endpoints are copied to a temp directory and run locally on the endpoint.
SMB Purpose for Windows Management:
According to the HPS Inspection Engine guide:
"Server Message Block (SMB) is a protocol for file and resource sharing. CounterACT uses this protocol with WMI or RPC methods to inspect and manage endpoints. This protocol must be available to perform the following:
Resolve file-related properties
Resolve script properties
Run script actions"
Script Execution Process Using SMB:
According to the documentation:
When WMI is used for Remote Inspection:
CounterACT downloads scripts - Scripts are transferred FROM CounterACT TO the endpoint using SMB protocol
Scripts stored in temp directory - By default, scripts are downloaded to and run from:
Non-interactive scripts: %TEMP%\fstmp\ directory
Interactive scripts: %TEMP% directory of currently logged-in user
Scripts execute locally - Scripts are executed ON the endpoint itself (not remotely executed from CounterACT)
Script Execution Locations:
According to the detailed documentation:
For Remote Inspection on Windows endpoints:
text
Non-interactive scripts are downloaded to and run from:
%TEMP%\fstmp\
(Typically %TEMP% is c:\windows\temp\)
Interactive scripts are downloaded to and run from:
%TEMP% directory of the currently logged-in user
For SecureConnector on Windows endpoints:
text
When deployed as a Service:
%TEMP%\fstmpsc\
When deployed as a Permanent Application:
%TEMP% directory of the currently logged-in user
SMB Requirements for Script Execution:
According to the documentation:
To execute scripts via SMB on Windows endpoints:
Port Requirements:
Windows 7 and above: Port 445/TCP
Earlier versions (XP, Vista): Port 139/TCP
Required Services:
Server service
Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
Remote Registry service
SMB Signing (optional but recommended):
Can be configured to require digitally signed SMB communication
Helps prevent SMB relay attacks
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Scripts run on CounterACT are copied to a temp directory and run locally on the endpoint - Scripts don't RUN on CounterACT; they're copied FROM CounterACT TO the endpoint
B. Scripts run on endpoints are copied to a Linux script repository - Forescout endpoints are Windows machines, not Linux; also no "Linux script repository" is involved
C. Scripts run on endpoints are copied to a temp directory and run remotely from CounterACT - Scripts run LOCALLY on the endpoint, not remotely from CounterACT
D. Scripts run on CounterACT are copied to a script repository and run remotely from CounterACT - Inverts the direction; CounterACT doesn't copy TO a repository; it copies TO endpoints
Script Execution Flow:
According to the documentation:
text
CounterACT --> (copies via SMB) --> Endpoint Temp Directory --> (executes locally) --> Result
The SMB protocol is essential for this file transfer step, which is why it's required for Windows manageability and script execution.
Referenced Documentation:
CounterACT Endpoint Module HPS Inspection Engine Configuration Guide v10.8
Script Execution Services documentation
About SMB documentation
When configuring policies, which of the following statements is true regarding this image?

The NOT checkbox means the "Evaluate Irresolvable as" should be set to True
The external NOT does not change the meaning of "evaluate irresolvable as"
Has no effect on irresolvable hosts
Negates the criteria inside the property
The NOT checkbox means the "Evaluate Irresolvable as" should be set to False
The NOT checkbox negates the criteria inside the property. According to the Forescout Administration Guide, when the NOT checkbox is selected on a policy condition criteria, it reverses the logic of that specific criterion evaluation.
Understanding the NOT Operator in Policy Conditions:
In Forescout policy configuration, the NOT operator is a Boolean logic operator that inverts the result of the property evaluation. When you select the NOT checkbox:
Logical Inversion - The condition is evaluated normally, and then the result is inverted
Criteria Negation - If a criteria would normally match an endpoint, selecting NOT causes it NOT to match
Property-Level Operation - The NOT operator applies specifically to that individual property/criterion, not to the entire rule
Example of NOT Logic:
Without NOT:
Condition: "Windows Antivirus Running = True"
Result: Matches endpoints that HAVE antivirus running
With NOT:
Condition: "NOT (Windows Antivirus Running = True)"
Result: Matches endpoints that DO NOT have antivirus running
NOT vs. "Evaluate Irresolvable As":
According to the documentation, the NOT operator and "Evaluate Irresolvable As" are independent settings:
NOT operator - Negates/inverts the criteria evaluation itself
"Evaluate Irresolvable As" - Defines what happens when a property CANNOT be resolved (is irresolvable)
These serve different purposes:
NOT determines what value to match
Evaluate Irresolvable As determines how to handle unresolvable properties
Handling Irresolvable Criteria:
According to the administration guide documentation:
"If you do not select the Evaluate irresolvable criteria as option, the criteria is handled as irresolvable and the endpoint does not undergo further analysis."
The "Evaluate Irresolvable As" checkbox allows you to define whether an irresolvable property should be treated as True or False when the property value cannot be determined. This is independent of the NOT checkbox.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. The NOT checkbox means the "Evaluate Irresolvable as" should be set to True - Incorrect; NOT and Evaluate Irresolvable As are independent settings
B. The external NOT does not change the meaning of "evaluate irresolvable as" - While technically true that NOT doesn't change the Evaluate Irresolvable setting, the answer doesn't explain what NOT actually does
C. Has no effect on irresolvable hosts - Incorrect; NOT negates the criterion logic regardless of whether it's resolvable
E. The NOT checkbox means the "Evaluate Irresolvable as" should be set to False - Incorrect; NOT and Evaluate Irresolvable As are independent
Policy Condition Structure:
According to the documentation, a policy condition consists of:
Property criteria combined with Boolean logic operators
Individual criterion settings including NOT operator
Irresolvable handling options that are separate from the NOT operator
Referenced Documentation:
Forescout Administration Guide - Define policy scope
Forescout eyeSight policy sub-rule advanced options
Handling Irresolvable Criteria section
Working with Policy Conditions
When using the "Assign to VLAN action," why might it be useful to have a policy to record the original VLAN?
Select one:
Since CounterACT reads the startup config to find the original VLAN, network administrators making changes to switch running configs could overwrite this VLAN information
Since CounterACT reads the running config to find the original VLAN, network administrators saving configuration changes to switches could overwrite this VLAN information
Since CounterACT reads the running config to find the original VLAN, network administrators making changes to switch running configs could overwrite this VLAN information
Since CounterACT reads the running config to find the original VLAN, any changes to switch running configs could overwrite this VLAN information
Since CounterACT reads the startup config to find the original VLAN, network administrators saving configuration changes to switches could overwrite this VLAN information
According to the Forescout Switch Plugin documentation, the correct answer is: "Since CounterACT reads the running config to find the original VLAN, any changes to switch running configs could overwrite this VLAN information".
Why Recording Original VLAN is Important:
According to the documentation:
When CounterACT assigns an endpoint to a quarantine VLAN:
Reading Original VLAN - CounterACT reads the switch running configuration to determine the original VLAN
Temporary Change - The endpoint is moved to the quarantine VLAN
Restoration Issue - If network administrators save configuration changes to the running config, CounterACT's reference to the original VLAN may be overwritten
Solution - Recording the original VLAN in a policy ensures you have a backup reference
Why Option D is the Most Accurate:
Option D states the key issue clearly: "any changes to switch running configs could overwrite this VLAN information." This is the most comprehensive and accurate statement because it acknowledges that ANY changes (not just those by administrators specifically) could cause the issue.
Which of the following logs are available from the GUI?
Host Details, Policy, Blocking, Event Viewer, Audit Trail
Switch, Policy, Blocking, Event Viewer, Audit Trail
Switch, Discovery, Threat Protection, Event Viewer, Audit Trail
HPS, Policy, Threat Protection, Event Viewer, Audit Trail
Host Details, Policy, Today Log, Threat Event Viewer, Audit Trail
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Forescout Platform Administration Guide, the logs available from the GUI Console include: Host Details, Policy, Blocking, Event Viewer, and Audit Trail.
Available Logs from the Forescout Console GUI:
Host Details Log - Provides detailed information about individual endpoints discovered on the network. This log displays comprehensive host properties and status information directly accessible from the console.
Policy Log - Shows policy activity and records how specific endpoints are handled by policies. The Policy Log investigates endpoint activity, displaying information about policy matches, actions executed, and policy evaluation results.
Blocking Log - Displays all blocking events that occur on the network, including port blocks, host blocks, and external port blocks. This log provides an at-a-glance display of blocked endpoints with timestamps and reasons.
Event Viewer - A system log that displays severity, date, status, element, and event information. Administrators can search, export, and filter events using the Event Viewer.
Audit Trail - Records administrative actions and changes made to the Forescout platform configuration and policies.
How to Access Logs from the GUI:
From the Forescout Console GUI, administrators access logs through the Log menu by selecting:
Blocking Logs to view block events
Event Viewer to display system events
Policy Reports to investigate policy activity
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
B. Switch, Policy, Blocking, Event Viewer, Audit Trail - "Switch" is not a standalone log type available from the GUI; switch data is captured through plugin logs and reports
C. Switch, Discovery, Threat Protection, Event Viewer, Audit Trail - "Discovery" and "Threat Protection" are report categories, not GUI logs in the standard log menu
D. HPS, Policy, Threat Protection, Event Viewer, Audit Trail - HPS logs are accessed through CLI, not the GUI; "Threat Protection" is a report, not a GUI log
E. Host Details, Policy, Today Log, Threat Event Viewer, Audit Trail - "Today Log" and "Threat Event Viewer" are not standard log names in the Forescout GUI
Referenced Documentation:
Forescout Platform Administration Guide - Generating Reports and Logs
Policy Reports and Logs section
Work with System Event Logs documentation
View Block Events documentation
When configuring policy conditions, which of the statements is true regarding this image?

Select one:
Negates the criteria as part of the property
Modifies the irresolvable condition to TRUE
Generates a NOT condition in the sub-rule condition
Irresolvable hosts would match the condition
Modifies the evaluate irresolvable condition to FALSE
Based on the policy condition image showing "Does not meet the following criteria", the correct statement is that it negates the criteria as part of the property.
Understanding "Does not meet the following criteria":
According to the Forescout Administration Guide:
The "Does not meet the following criteria" radio button option in policy conditions creates a logical negation of the condition:
"Meets the following criteria" - Endpoint matches if the condition is true
"Does not meet the following criteria" - Endpoint matches if the condition is FALSE (negated)
How the Negation Works:
According to the documentation:
"Use the AND value between both properties: Windows>Manageable Domain>Does not meet the following criteria"
This syntax shows that "Does not meet the following criteria" negates the entire criteria evaluation:
Normal condition: "Windows Antivirus Running = True"
Result: Matches endpoints WITH antivirus running
Negated condition: "Windows Antivirus Running Does not meet the following criteria (= True)"
Result: Matches endpoints WITHOUT antivirus running (negates the criteria)
Negation Happens at Property Level:
The negation is applied as part of the property evaluation, not as a separate NOT operator. When you select "Does not meet the following criteria":
The condition is evaluated normally
The result is then negated/inverted
The endpoint matches only if the negated result is true
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
B. Modifies the irresolvable condition to TRUE - "Does not meet the following criteria" doesn't specifically affect irresolvable property handling
C. Generates a NOT condition in the sub-rule condition - The negation is part of this property's evaluation, not a separate sub-rule NOT condition
D. Irresolvable hosts would match the condition - "Does not meet the following criteria" doesn't specifically target irresolvable hosts
E. Modifies the evaluate irresolvable condition to FALSE - This setting doesn't affect the "Evaluate irresolvable as" setting
Referenced Documentation:
Forescout Administration Guide v8.3
Forescout Administration Guide v8.4
ForeScout CounterACT Administration Guide - Policy Conditions section
Manage Actions documentation
Main rules are executed independently of each other. However, one policy may be set to run first by configuring which of the following?
There is no way to cause one policy to run first
Setting the Main Rule condition to utilize primary classification
Categorizing the Policy as an assessment policy
Categorizing the Policy as a classifier
Using Irresolvable criteria
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Forescout Administration Guide, one policy can be set to run first by categorizing the Policy as a classifier. Classifier policies run before other policy types.
Policy Categorization and Execution Order:
According to the Forescout Administration Guide:
Forescout supports different policy categories, and these categories determine execution order:
Classifier Policies - Run FIRST
Used for initial device classification
Establish basic device properties (OS, Function, Network Function)
Must complete before other policies can evaluate classification properties
Assessment Policies - Run AFTER classifiers
Assess compliance based on classified properties
Depend on classifier output
Control/Action Policies - Run LAST
Apply remediation actions
Depend on assessment results
How Classifier Policies Run First:
According to the documentation:
"When you categorize a policy as a classifier, it runs before assessment and action policies. This allows the classified properties to be established before other policies attempt to evaluate them."
Reason for Classifier Priority:
According to the policy execution guidelines:
Classifier policies must run first because:
Dependency Resolution - Other policies depend on classification properties
Property Population - Classifiers populate device properties used by other policies
Execution Efficiency - Classifiers determine what type of device is being evaluated
Logical Flow - You must know what a device is before assessing or controlling it
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. There is no way to cause one policy to run first - Incorrect; categorization determines execution order
B. Setting Main Rule condition to utilize primary classification - While main rule conditions can reference classification, this doesn't change policy execution order
C. Categorizing the Policy as an assessment policy - Assessment policies run AFTER classifier policies, not first
E. Using Irresolvable criteria - Irresolvable criteria handling doesn't affect policy execution order
Policy Categorization Example:
According to the documentation:
text
Policy Execution Order:
1. CLASSIFIER Policies (Run First)
- "Device Classification Policy" (categorized as Classifier)
- Resolves: OS, Function, Network Function
2. ASSESSMENT Policies (Run Second)
- "Windows Compliance Policy" (categorized as Assessment)
- Depends on classification from step 1
3. ACTION Policies (Run Last)
- "Remediate Non-Compliant Devices" (categorized as Control)
- Depends on assessment from step 2
In this workflow, because "Device Classification Policy" is categorized as a Classifier, it executes first, populating device properties that the subsequent Assessment and Action policies need.
Referenced Documentation:
ForeScout CounterACT Administration Guide - Policy Categorization
Categorize Endpoint Authorizations - Policy Categories and Execution
Which of the following User Directory server settings is necessary to enable guest approval by sponsors?
Policy to control
Guest Tags
Sponsor Group
Guest password policy
Authentication Server
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
The Sponsor Group is the necessary User Directory server setting required to enable guest approval by sponsors. According to the Forescout User Directory Plugin Configuration Guide and Guest Management Portal documentation, Sponsor Groups must be created and configured to define the corporate employees (sponsors) who are authorized to approve or decline guest network access requests.
Sponsor Group Configuration:
In the Guest Management pane, the Sponsors tab is used to define the corporate employees who are authorized to log into the Guest Management Portal to approve network access requests from guests. These employees are assigned to specific Sponsor Groups, which control which sponsors can approve guest access requests.
How Sponsor Groups Enable Guest Approval:
Sponsor Definition - Corporate employees must be designated as sponsors and assigned to a Sponsor Group
Approval Authority - Sponsors in assigned groups can approve or decline guest network access requests
Authentication - When "Enable sponsor approval without authentication via emailed link" is selected, sponsors in the designated group can approve guests based on email link authorization
Guest Registration - Guest registration options connect Sponsor Groups to the guest approval workflow
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Policy to control - While policies are used for guest control, they do not define which sponsors can approve guests
B. Guest Tags - Guest Tags are used to classify and organize guest accounts, not to enable sponsor approval
D. Guest password policy - This setting controls password requirements for guests, not sponsor approval authority
E. Authentication Server - Authentication servers verify credentials but do not establish sponsor approval groups
Referenced Documentation:
Forescout User Directory Plugin Configuration Guide - Create Sponsors section
Guest Management Portal - Sponsor Configuration documentation
"Create sponsors" - Forescout Administration Guide section
Why would the patch delivery optimization mechanism used for Windows 10 updates be a potential security concern?
It can be configured to use a peer-to-peer file sharing protocol
CounterACT cannot initiate Windows updates for Windows 10 devices
It uses a peer-to-peer file sharing protocol by default
The registry DWORD controlling this behavior cannot be changed
It always uses a peer-to-peer file sharing protocol
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Windows Update Delivery Optimization documentation and security analysis, the potential security concern with patch delivery optimization for Windows 10 updates is that it CAN BE CONFIGURED to use a peer-to-peer file sharing protocol. While the feature includes security mechanisms like cryptographic signing, the capability to enable P2P sharing does create potential security concerns depending on the configuration.
Windows Update Delivery Optimization Overview:
According to the Windows Delivery Optimization documentation:
"Windows Update Delivery Optimization is a feature in Microsoft's Windows designed to improve the efficiency of downloading and distributing updates. Instead of each device independently downloading updates from Microsoft's servers, Update Delivery Optimization allows devices to share update files with each other, either within a local network or over the internet. This peer-to-peer (p2p) approach reduces bandwidth consumption and accelerates the update process."
Configuration Flexibility:
According to the documentation:
The P2P feature is configurable, not mandated:
Default Setting - By default, Delivery Optimization is enabled for local network sharing
Configurable Options:
PCs on my local network only (safer)
PCs on my local network and the internet (broader sharing, higher risk)
Disabled entirely
Security Concerns Related to P2P Configuration:
According to the security analysis:
When P2P is enabled, potential concerns include:
Network Isolation Risks - In firewalled or segmented networks, P2P discovery can expose endpoints
Bandwidth Consumption - Improperly configured P2P can saturate network resources
Peer Discovery Vulnerabilities - Devices must discover each other, potentially exposing endpoints
Internet-based Sharing Risks - When "internet peers" are enabled, updates are shared across the internet
Privacy Implications - Devices communicating for update sharing may leak information
Cryptographic Protection Does NOT Eliminate Configuration Risk:
According to the documentation:
"While Update Delivery Optimization ensures that all update files are cryptographically signed and verified before installation, some organizations may still be concerned about allowing peer-to-peer data sharing."
While the updates themselves are protected, the act of enabling P2P configuration creates the security concern.
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
B. CounterACT cannot initiate Windows updates for Windows 10 - Incorrect; CounterACT can initiate Windows updates; this is not the security concern
C. It uses peer-to-peer by default - Incorrect; while enabled by default for local networks, internet P2P sharing requires explicit configuration
D. The registry DWORD cannot be changed - Incorrect; the DO modes registry value (DODownloadMode) CAN be changed via GPO or registry
E. It always uses peer-to-peer - Incorrect; P2P is configurable, not mandatory; organizations can disable it entirely
Registry DWORD Configuration Options:
According to the Windows documentation:
The DODownloadMode DWORD value can be configured to:
0 = HTTP only, no peering (addresses security concern)
1 = HTTP blended with local peering (moderate risk)
3 = HTTP blended with internet peering (higher risk - the security concern)
99 = Simple download mode
This demonstrates that P2P can be configured, which is the security concern mentioned in the question.
Referenced Documentation:
What is Windows Update Delivery Optimization - Scalefusion Blog
Windows Delivery Optimization: Risks & Challenges - LinkedIn Article
Introduction to Windows Update Delivery Optimization - Sygnia Analysis
Which of the following switch actions cannot both be used concurrently on the same switch?
Access Port ACL & Switch Block
Switch Block & Assign to VLAN
Endpoint Address ACL & Assign to VLAN
Access Port ACL & Endpoint Address ACL
Access Port ACL & Assign to VLAN
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Forescout Switch Plugin Configuration Guide, Access Port ACL and Endpoint Address ACL cannot both be used concurrently on the same endpoint. These two actions are mutually exclusive because they both apply ACL rules to control traffic, but through different mechanisms, and attempting to apply both simultaneously creates a conflict.
Switch Restrict Actions Overview:
The Forescout Switch Plugin provides several restrict actions that can be applied to endpoints:
Access Port ACL - Applies an operator-defined ACL to the access port of an endpoint
Endpoint Address ACL - Applies an operator-defined ACL based on the endpoint's address (MAC or IP)
Assign to VLAN - Assigns the endpoint to a specific VLAN
Switch Block - Completely isolates endpoints by turning off their switch port
Action Compatibility Rules:
According to the Switch Plugin Configuration Guide:
Endpoint Address ACL vs Access Port ACL - These CANNOT be used together on the same endpoint because:
Both actions modify switch filtering rules
Both actions can conflict when applied simultaneously
The Switch Plugin cannot determine priority between conflicting ACL configurations
Applying both would create ambiguous filtering logic on the switch
Actions That CAN Be Used Together:
Access Port ACL + Assign to VLAN -✓Can be used concurrently
Endpoint Address ACL + Assign to VLAN -✓Can be used concurrently
Switch Block + Assign to VLAN - This is semantically redundant (blocking takes precedence) but is allowed
Access Port ACL + Switch Block -✓Can be used concurrently (though Block takes precedence)
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Access Port ACL & Switch Block - These CAN be used concurrently; Switch Block would take precedence
B. Switch Block & Assign to VLAN - These CAN be used concurrently (though redundant)
C. Endpoint Address ACL & Assign to VLAN - These CAN be used concurrently
E. Access Port ACL & Assign to VLAN - These CAN be used concurrently; they work on different aspects of port management
ACL Action Definition:
According to the documentation:
Access Port ACL - "Use the Access Port ACL action to define an ACL that addresses one or more than one access control scenario, which is then applied to an endpoint's switch port"
Endpoint Address ACL - "Use the Endpoint Address ACL action to apply an operator-defined ACL, addressing one or more than one access control scenario, which is applied to an endpoint's address"
Referenced Documentation:
Forescout CounterACT Switch Plugin Configuration Guide Version 8.12
Switch Plugin Configuration Guide v8.14.2
Switch Restrict Actions documentation
What is the default recheck timer for a NAC policy?
24 hours
8 hours
4 hours
12 hours
2 hours
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Forescout Administration Guide - Policy Main Rule Advanced Options, the default recheck timer for a NAC policy is 8 hours.
Default Policy Recheck Timer:
According to the official documentation:
"By default, both matched endpoints and unmatched endpoints are rechecked every eight hours, and on any admission event."
This 8-hour default ensures that all endpoints are periodically re-evaluated against policy conditions, regardless of whether they currently match the policy.
Recheck Configuration:
According to the documentation:
When you configure a policy's main rule advanced options:
Default Recheck Interval: 8 hours
Customizable Range: Can be configured from 1 hour to infinite (no recheck)
Applies to: All endpoints in the policy scope
Recheck Triggers:
According to the administration guide:
Policies recheck when:
Recheck Timer Expires - Every 8 hours by default
Admission Event - When specific network events occur
SecureConnector Event - When SC status changes
Referenced Documentation:
Forescout Platform Policy Main Rule Advanced Options
Main Rule Advanced Options
The host property 'HTTP User Agent banner' is resolved by what function?
Device classification engine
NetFlow
NMAP scanning
Packet engine
Device profile library
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Forescout Administration Guide - Advanced Classification Properties, the host property "HTTP User Agent banner" is resolved by the Packet Engine.
HTTP User Agent Banner Property:
According to the Advanced Classification Properties documentation:
The HTTP User Agent property is captured through passive network traffic analysis by the Packet Engine, which monitors and analyzes HTTP headers in network traffic.
Packet Engine Function:
According to the Packet Engine documentation:
The Packet Engine provides:
Passive Traffic Monitoring - Analyzes network packets without interfering
HTTP Header Analysis - Extracts HTTP headers from captured traffic
User Agent Detection - Identifies HTTP User Agent strings from web requests
Property Resolution - Populates device properties from observed traffic
HTTP User Agent Examples:
Common User Agent banners that identify device types and browsers:
text
Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36
Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; CPU iPhone OS 14_6 like Mac OS X) AppleWebKit/605.1.15
Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 11; SM-G991B) AppleWebKit/537.36
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Device classification engine - The classification engine uses properties resolved by other components like the Packet Engine
B. NetFlow - NetFlow provides flow statistics, not application-level data like HTTP headers
C. NMAP scanning - NMAP performs active port scanning, not passive HTTP header analysis
E. Device profile library - The profile library uses properties; it doesn't resolve them
Property Resolution by Function:
According to the documentation:
Property
Packet Engine
NMAP
Device Class Engine
Profile Library
HTTP User Agent
✓Yes
✗No
✗No
✗No
Service Banner
✗No
✓Yes
✗No
✗No
OS Classification
Partial
Partial
✓Yes
✗No
Function
✗No
✗No
✓Yes
✓Yes
Referenced Documentation:
Advanced Classification Properties
About the Packet Engine
Forescout Platform Dependencies and Known Issues
What is the best practice to pass an endpoint from one policy to another?
Use operating system property
Use sub rules
Use function property
Use groups
Use policy condition
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment Documentation, the best practice to pass an endpoint from one policy to another is to use SUB-RULES.
Sub-Rules and Policy Routing:
Sub-rules are conditional branches within a Forescout policy that allow for sophisticated endpoint routing and handling. When an endpoint matches a sub-rule condition, it can be directed to perform specific actions or be passed to another policy group for further evaluation.
Key Advantages of Using Sub-Rules:
Granular Control - Sub-rules enable precise segmentation of endpoints based on multiple properties and conditions
Hierarchical Processing - Once an endpoint matches a sub-rule, it proceeds down the sub-rule branch; later sub-rules of the policy are not evaluated for that endpoint
Efficient Endpoint Routing - Sub-rules allow endpoints to be efficiently routed to appropriate policy handlers without evaluating unnecessary conditions
Policy Chaining - Sub-rules facilitate the logical flow and routing of endpoints through multiple policy layers
Best Practice Implementation:
The documentation emphasizes that when designing policies for endpoint management, administrators should:
Use sub-rules to create conditional branches that evaluate endpoints against multiple criteria
Route endpoints to appropriate policy handlers based on their properties and compliance status
Avoid using simple property-based routing when complex multi-step evaluation is needed
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Use operating system property - While OS properties can be used in conditions, they are not the mechanism for passing endpoints between policies
C. Use function property - Function properties are not used for inter-policy endpoint routing
D. Use groups - While groups are useful for organizing endpoints, they are not the primary best practice for passing endpoints between policies
E. Use policy condition - Policy conditions define what endpoints should be evaluated, but sub-rules provide the actual routing mechanism
Referenced Documentation:
Forescout Platform Administration Guide - Defining Policy Sub-Rules
"Defining Forescout Platform Policy Sub-Rules" - Best Practice section
Sub-Rule Advanced Options documentation
Which type of endpoint can be queried for registry key properties?
Managed unknown endpoint
Unmanaged Windows endpoint
Managed Windows endpoint
Windows endpoint
Managed Linux endpoint
Comprehensive and Detailed Explanation From Exact Extract of Forescout Platform Administration and Deployment:
According to the Forescout Administration Guide - Set Registry Key on Windows action, registry key properties can only be queried on "Managed Windows endpoints".
Registry Key Property Requirements:
According to the Set Registry Key on Windows documentation:
"Registry key properties can be queried on managed Windows endpoints only. The endpoint must be a Windows device that is managed (either via SecureConnector deployment or Remote Inspection with appropriate credentials)."
Managed vs. Unmanaged Endpoints:
According to the Windows Properties documentation:
Managed Windows Endpoint -✓Can query registry keys
Has SecureConnector deployed, OR
Has Remote Inspection access via credentials, OR
Is domain-joined with appropriate permissions
Unmanaged Windows Endpoint -✗Cannot query registry keys
No agent or access method available
Registry cannot be accessed remotely
Why Other Options Are Incorrect:
A. Managed unknown endpoint - "Unknown" endpoints are not classified as Windows; classification unknown
B. Unmanaged Windows endpoint - Unmanaged endpoints have no access to registry
D. Windows endpoint - Must be "managed" to query registry; not all Windows endpoints are managed
E. Managed Linux endpoint - Linux systems don't have Windows registry
Registry Access Methods:
According to the documentation:
Registry keys can be queried on Managed Windows endpoints using:
SecureConnector - Preferred method for interactive registry access
Remote Inspection (MS-WMI/RPC) - When credentials are configured
Domain Credentials - When endpoint is domain-joined
Referenced Documentation:
Set Registry Key on Windows - v9.1.4
Set Registry Key on Windows - v8.5.2
Windows Properties

TESTED 20 Feb 2026

