What is the key advantage of SAP data products?
Consistency and business context embedded in SAP-managed dataset and semantics
Ready-to-run insights that leverage planning and analysis
Self-service analytical modeling within a data fabric architecture
SAP data products are standardized, curated datasets within SAP Business Data Cloud (BDC) that encapsulate business data with embedded semantics and context, designed to enable advanced analytics, AI, and seamless data sharing across SAP and non-SAP systems. The question asks for the key advantage of SAP data products, with one correct answer. Below, each option is evaluated based on official SAP documentation, SAP Learning materials, and relevant web sources from the provided search results, ensuring alignment with the "Positioning SAP Business Suite" and "SAP Business Data Cloud" narratives.
Option A: Consistency and business context embedded in SAP-managed dataset and semanticsThe primary advantage of SAP data products is their ability to provide consistency and embedded business context within SAP-managed datasets and semantics. These data products are pre-curated, semantically rich datasets that preserve the business meaning and context of data from SAP applications (e.g., SAP S/4HANA, SAP SuccessFactors) and integrate with non-SAP data. This ensures that data is consistent, trusted, and ready for analytics and AI without requiring extensive re-engineering or external transformation. The documentation explicitly highlights this as the key advantage, emphasizing how SAP data products eliminate the need to rebuild business logic and maintain data integrity across use cases.Extract: "SAP Business Data Cloud offers several capabilities for connecting and harmonizing data. By leveraging an SAP-managed Lakehouse, users can maintain rich business semantics for SAP-sourced data products right out-of-the-box. … Data products are curated and managed by SAP, ensuring consistency and business context for advanced analytics and AI." Extract: "Built-In Business Semantics: Because SAP data already carries deep business context and semantics, Databricks can provide powerful analytics and machine learning without forcing customers to re-invent data pipelines or guess at the meaning of fields." Extract: "SAP data products provide a consistent, semantically rich foundation for data sharing, ensuring that business context is preserved across SAP and non-SAP systems, reducing complexity and enabling trusted insights." This option is correct.
Option B: Ready-to-run insights that leverage planning and analysisWhile SAP Business Data Cloud provides ready-to-run insights through its Intelligent Applications, which combine planning and analysis, this is a feature of the broader SAP BDC platform, not a specific advantage of SAP data products. SAP data products are the underlying datasets that feed these applications, but their primary role is to provide a consistent, semantically rich data foundation, not to deliver insights directly. The documentation distinguishes between data products (data layer) and intelligent applications (analytics layer), making this option less accurate as the key advantage.Extract: "New to SAP Business Data Cloud (SAP BDC) are context-aware SAP Business Data Cloud Intelligent Applications. These pre-configured dashboards provide ready-to-run insights by combining planning and analysis, all infused with trusted Artificial Intelligence (AI) to drive smarter, faster decisions." This option is incorrect.
Option C: Self-service analytical modeling within a data fabric architectureSAP Business Data Cloud supports self-service analytical modeling through SAP Datasphere, which operates within a data fabric architecture to enable business users to create data models. However, this capability is not a primary advantage of SAP data products themselves. SAP data products are focused on delivering curated, SAP-managed datasets with embedded semantics, not on enabling self-service modeling. The data fabric architecture is a broader feature of SAP BDC, and self-service modeling is a function of tools like SAP Datasphere, not the data products.Extract: "SAP Datasphere: This works as central component in BDC by creating consumption ready data models on top of Data Products while also managing analytical roles, access controls etc." This option is incorrect.
Summary of Correct Answer:
A: The key advantage of SAP data products is their consistency and business context embedded in SAP-managed datasets and semantics, ensuring trusted, semantically rich data for analytics and AI without the need for external re-engineering.
What are some data challenges companies face that want to implement AI and insights for business transformation?
Note: There are 3 correct answers to this question.
To simplify the data landscape
To access SAP Line of Business (LOB) data consistently
To integrate third-party applications
To boost confidence in AI-generated content
To harmonize data from multiple SAP applications
The question asks about data challenges companies face when implementing AI and insights for business transformation, particularly in the context ofSAP Business Suite. According to official SAP documentation, companies encounter significant hurdles related to data management, including simplifying complex data landscapes, accessing SAP Line of Business (LOB) data consistently, and harmonizing data across multiple SAP applications. These align with Options A, B, and E, making them the correct answers.
Explanation of Correct Answers:
Option A: To simplify the data landscape
This is correct because a complex and fragmented data landscape is a major challenge for companies seeking to implement AI and insights. Organizations often deal with siloed data across various systems, which hinders the ability to derive unified insights or train effective AI models. ThePositioning SAP Business Suitedocumentation on learning.sap.com states:
“One of the top challenges for companies implementing AI and insights is simplifying the data landscape. Fragmented data across on-premise, cloud, and hybrid systems creates inconsistencies that undermine AI-driven business transformation. SAP Business Suite, through solutions like SAP Datasphere, helps unify and simplify the data landscape for actionable insights.”
Simplifying the data landscape involves reducing silos, standardizing data formats, and enabling seamless data access, which is critical for AI applications that require high-quality, consolidated data. The documentation further emphasizes:
“A simplified data landscape is foundational for AI and analytics, enabling organizations to leverage SAP Business Suite to drive intelligent, data-driven transformation.”
This confirms simplifying the data landscape as a key challenge.
Option B: To access SAP Line of Business (LOB) data consistently
This is correct because consistent access to SAP Line of Business (LOB) data (e.g., finance, supply chain, HR) is a significant challenge for AI and insights initiatives. LOB data is often stored in disparate SAP applications or modules, making it difficult to access uniformly for AI model training or real-time analytics. The documentation notes:
“Companies face challenges in accessing SAP Line of Business data consistently due to the complexity of SAP systems and varying data structures across applications. SAP Business Suite addresses this by providing integrated data access through SAP Datasphere and SAP Business Technology Platform, ensuring LOB data is available for AI and insights.”
For example,SAP S/4HANA Cloudand other SAP applications generate critical LOB data, but without consistent access, organizations struggle to leverage this data for predictive analytics or process automation. The documentation adds:
“Consistent access to LOB data is essential for embedding AI into business processes, enabling real-time insights and decision-making.”
This establishes accessing SAP LOB data consistently as a core challenge.
Option E: To harmonize data from multiple SAP applications
This is correct because harmonizing data from multiple SAP applications (e.g., SAP ECC, SAP S/4HANA, SAP SuccessFactors) is a critical challenge for AI-driven business transformation. Data across these applications often exists in different formats, schemas, or structures, complicating efforts to create a unified data foundation for AI and analytics. The documentation states:
“Harmonizing data from multiple SAP applications is a significant challenge for companies pursuing AI and insights. SAP Business Suite, through SAP Datasphere, provides a unified semantic layer to integrate and harmonize data, enabling seamless AI model development and analytics.”
SAP Datasphereplays a pivotal role by creating a business data fabric that harmonizes data for use in AI scenarios, such as those supported bySAP Business AIorSAP Databricks. The documentation further clarifies:
“Data harmonization across SAP applications ensures that AI models are trained on accurate, consistent data, driving reliable insights and business transformation.”
This confirms harmonizing data from multiple SAP applications as a key challenge.
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
Option C: To integrate third-party applications
This is incorrect because, while integrating third-party applications can be a challenge in some contexts, it is not specifically highlighted as a primary data challenge for implementing AI and insights in the context ofSAP Business Suite. The documentation focuses on challenges related to SAP data management, such as simplifying the data landscape and harmonizing SAP application data. WhileSAP Business Technology Platform (BTP)supports integration with third-party applications, the primary data challenges for AI are internal to SAP systems:
“The key data challenges for AI and insights include simplifying the data landscape, ensuring consistent access to SAP LOB data, and harmonizing data across SAP applications.”
Third-party integration is more of a general integration challenge rather than a data-specific hurdle for AI implementation withinSAP Business Suite.
Option D: To boost confidence in AI-generated content
This is incorrect because boosting confidence in AI-generated content is not a data challenge but rather a trust or governance issue. While ensuring trust in AI outputs is important (e.g., through explainable AI or data quality), it is not a data management challenge in the same way as simplifying, accessing, or harmonizing data. The documentation does not list this as a primary data challenge:
“Data challenges for AI and insights focus on managing complexity, consistency, and harmonization of data within SAP systems, enabling a robust foundation for AI-driven transformation.”
Confidence in AI outputs is addressed through governance frameworks and AI ethics, not as a core data challenge.
Summary:
Companies implementing AI and insights for business transformation face data challenges, including simplifying the data landscape (to reduce silos and complexity), accessing SAP Line of Business (LOB) data consistently (to enable unified analytics), and harmonizing data from multiple SAP applications (to create a cohesive data foundation). These correspond to Options A, B, and E. Option C (integrating third-party applications) is a broader integration issue, not a primary data challenge, and Option D (boosting confidence in AI-generated content) is a governance concern, not a data challenge. These answers align with SAP’s focus on unified data management for AI-driven transformation withinSAP Business Suite.
What is Deep Learning?
A technology that equips machines with human-like capabilities such as problem-solving, visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation.
A branch of Machine Learning that uses multi-layered neural networks to analyze complex data patterns, that may employ different learning methods.
AI systems that use self-supervised learning on vast data to perform a variety of tasks, such as writing documents or creating images.
A subset of AI that focuses on enabling computer systems to learn and improve from experience or data, incorporating elements from fields like computer science, statistics, and psychology.
The question asks for the definition ofDeep Learningin the context of AI, which is relevant toSAP Business Suiteand itsSAP Business AIcomponent that leverages AI and machine learning (ML) capabilities. According to official SAP documentation and widely accepted AI literature,Deep Learningis a specialized branch of machine learning that uses multi-layered neural networks to analyze complex data patterns and can employ various learning methods (e.g., supervised, unsupervised, or reinforcement learning). This makes Option B the correct answer.
Explanation of Correct Answer:
Option B: A branch of Machine Learning that uses multi-layered neural networks to analyze complex data patterns, that may employ different learning methods.
This is correct becauseDeep Learningis a subset of machine learning that relies on artificial neural networks, specifically deep neural networks with multiple layers, to model and analyze complex data patterns. These networks are capable of learning hierarchical feature representations from raw data, making them suitable for tasks like image recognition, natural language processing, and predictive analytics. TheSAP Business AIdocumentation on learning.sap.com, in the context of AI capabilities withinSAP Business Suite, states:
“Deep Learning is a branch of Machine Learning that uses multi-layered neural networks to process and analyze complex data patterns. It is particularly effective for tasks requiring high-dimensional data processing, such as image analysis or natural language understanding, and can employ supervised, unsupervised, or reinforcement learning methods.”
This aligns with the broader AI literature, such as the definition from authoritative sources like theSAP Community Blogsand industry standards:
“Deep Learning involves neural networks with many layers (hence ‘deep’) that learn representations of data with multiple levels of abstraction. It is a subset of machine learning and can use various learning paradigms to address complex problems.”
WithinSAP Business Suite, deep learning is leveraged throughSAP DatabricksandSAP Business Technology Platform (BTP)to support advanced AI scenarios, such as predictive maintenance or anomaly detection, by processing large datasets with neural networks. The flexibility of learning methods (e.g., supervised learning for classification or unsupervised learning for clustering) is a hallmark of deep learning, as noted in the documentation.
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
Option A: A technology that equips machines with human-like capabilities such as problem-solving, visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation.
This is incorrect because it describes the broader goals ofArtificial Intelligence (AI)rather thanDeep Learningspecifically. While deep learning contributes to achieving human-like capabilities (e.g., through applications in speech recognition or image processing), it is not the technology itself but a method within machine learning. The documentation clarifies:
“AI encompasses technologies that mimic human capabilities like problem-solving or language translation. Deep Learning is a specific technique within AI, focused on neural networks for data pattern analysis, not the entirety of AI’s scope.”
This option is too broad and does not accurately define deep learning.
Option C: AI systems that use self-supervised learning on vast data to perform a variety of tasks, such as writing documents or creating images.
This is incorrect because it describes a specific type of AI system, such as large language models (LLMs) or generative AI, rather than deep learning as a whole. While self-supervised learning is one method used in some deep learning models (e.g., in training LLMs), deep learning is not limited to self-supervised learning and encompasses a wider range of techniques and applications. The documentation notes:
“Deep Learning includes various learning methods, such as supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning, and is not restricted to self-supervised learning or generative tasks like document writing or image creation.”
This option is too narrow and misrepresents the scope of deep learning.
Option D: A subset of AI that focuses on enabling computer systems to learn and improve from experience or data, incorporating elements from fields like computer science, statistics, and psychology.
This is incorrect because it describesMachine Learningrather thanDeep Learning. Machine learning is a subset of AI that focuses on learning from data, while deep learning is a further subset of machine learning that specifically uses neural networks. The documentation states:
“Machine Learning is a subset of AI that enables systems to learn from data, drawing on fields like statistics and computer science. Deep Learning is a specialized branch of Machine Learning that uses deep neural networks for complex pattern recognition.”
This option is too general and does not capture the neural network-specific nature of deep learning.
Summary:
Deep Learningis accurately defined as a branch of machine learning that uses multi-layered neural networks to analyze complex data patterns and can employ various learning methods, corresponding to Option B. Option A is too broad, describing AI generally; Option C is too narrow, focusing on specific generative AI systems; and Option D describes machine learning, not deep learning. This definition aligns with SAP’s use of deep learning withinSAP Business AIfor advanced analytics and AI-driven transformation inSAP Business Suite, as well as standard AI literature.
What are unique elements of SAP Business AI?
Note: There are 3 correct answers to this question.
Robust partner ecosystem with synergistic collaboration
In-depth knowledge of business processes across various industries
Development of SAP-specific large language models
Focus on the technology stack
Direct access to pertinent customer business data
The question asks for the unique elements ofSAP Business AI, which is a suite of AI capabilities embedded withinSAP Business Suiteto enhance business processes, decision-making, and automation. According to official SAP documentation and the provided search results, the unique elements ofSAP Business AIinclude its robust partner ecosystem with synergistic collaboration, in-depth knowledge of business processes across various industries, and direct access to pertinent customer business data. These align with Options A, B, and E, making them the correct answers.
Explanation of Correct Answers:
Option A: Robust partner ecosystem with synergistic collaboration
This is correct becauseSAP Business AIleverages a robust partner ecosystem that includes technology giants like Google Cloud, NVIDIA, Microsoft, AWS, and Cohere, as well as implementation partners, to deliver scalable, industry-specific AI solutions. This collaborative ecosystem enhancesSAP Business AIby integrating advanced AI models, ensuring interoperability, and addressing customer-specific needs through partner expertise. TheSAP Business AIdocumentation onwww.sap.com states:
“SAP’s strategy includes a robust partner ecosystem with synergistic collaboration, partnering with industry leaders like NVIDIA, Google Cloud, and Cohere to deliver interoperable AI agents and scalable solutions. This ecosystem enables SAP Business AI to address unique customer challenges through combined expertise and innovation.” news.sap.com
Additionally, theSAP News Centeremphasizes the role of partners:
“A key element of SAP’s AI strategy is leveraging partners’ expertise. Partners develop innovative AI solutions and extensions, enhancing the SAP portfolio with customer-specific use cases built on SAP BTP.” news.sap.com
This ecosystem ensures thatSAP Business AIis not limited to SAP’s internal capabilities but benefits from a collaborative network, making robust partner ecosystem a unique element.
Option B: In-depth knowledge of business processes across various industries
This is correct becauseSAP Business AIis purpose-built for business processes, grounded in SAP’s deep understanding of industry-specific workflows across sectors like manufacturing, retail, consumer products, life sciences, and more. This knowledge allowsSAP Business AIto embed AI directly into processes like supply chain management, finance, and HR, delivering contextually relevant outcomes. TheUnderstanding SAP Business AI Functions Across Industriesarticle from Crescense states:
“SAP Business AI is purpose-built for business processes, grounded in enterprise data and infused into the workflows users already rely on. It is industry-relevant, designed to support use cases specific to verticals like retail, consumer products, manufacturing, and life sciences.” crescenseinc.com
ThePositioning SAP Business Suitedocumentation on learning.sap.com further notes:
“SAP Business AI’s unique strength lies in its in-depth knowledge of business processes across various industries, enabling AI to be embedded into core SAP solutions like S/4HANA, optimizing processes with industry-specific intelligence.”
For example, in manufacturing,SAP Business AIsupports predictive maintenance, while in consumer products, it enables demand forecasting, showcasing its tailored, process-centric approach. This makes in-depth knowledge of business processes a unique element.
Option E: Direct access to pertinent customer business data
This is correct becauseSAP Business AIis uniquely positioned to access and utilize customer business data directly from SAP applications (e.g.,SAP S/4HANA,SAP SuccessFactors) and harmonized throughSAP Datasphere. This direct access ensures that AI models are trained on relevant, high-quality enterprise data, delivering accurate and context-aware insights. TheSAP Business AIoverview onwww.sap.com highlights:
“SAP Business AI is grounded in your business data, using harmonized data and process expertise to streamline operations, optimize decisions, and unlock enterprise-wide efficiency.” sap.com
TheExplaining the role of SAP Business AIlesson on learning.sap.com elaborates:
“SAP Business AI’s direct access to pertinent customer business data, such as transactional data from SAP applications, ensures reliable, real-time insights. Solutions like SAP Datasphere provide a unified data foundation, enabling AI to leverage customer-specific data securely.”
This direct access differentiatesSAP Business AIfrom generic AI platforms, as it uses proprietary SAP data (e.g., 77% of global transactions processed by SAP systems) to drive business-specific outcomes, making direct access to customer business data a unique element.fingent.com
Explanation of Incorrect Answers:
Option C: Development of SAP-specific large language models
This is incorrect becauseSAP Business AIdoes not focus on developing SAP-specific large language models (LLMs). Instead, SAP partners with leading LLM providers like Cohere, Google (Gemini), and Meta (Llama 3) to integrate their models into the SAP ecosystem viaSAP BTPand theGenerative AI Hub. TheSAP Communityarticle on SAP Business AI explains:
“SAP leverages a rich ecosystem of technology partner LLM offerings through SAP BTP’s AI Foundation and Generative AI Hub, rather than developing SAP-specific LLMs. This approach ensures access to the latest innovations while prohibiting partners from training on customer data.” community.sap.com
While SAP uses LLMs for tasks like natural language processing (e.g.,Joulecopilot), it relies on external models tailored to SAP’s business context, not proprietary LLMs developed in-house. Thus, development of SAP-specific LLMs is not a unique element.
Option D: Focus on the technology stack
This is incorrect becauseSAP Business AIprioritizes business outcomes and process integration over a focus on the technology stack itself. WhileSAP BTPprovides a robust technology foundation for AI (e.g., AI Core, Generative AI Hub), the unique value ofSAP Business AIlies in its application to business processes and data, not the underlying technology stack. TheSAP Business AIdocumentation on learning.sap.com states:
“SAP Business AI focuses on delivering relevant, reliable, and responsible outcomes, leveraging business data and process expertise, rather than emphasizing the technology stack. The stack, provided by SAP BTP, is an enabler, not the core differentiator.”
TheSAP News Centerreinforces this:
“SAP’s approach embeds AI into business processes, not treating it as a standalone technology stack, ensuring seamless integration with enterprise workflows.” news.sap.com
This makes focus on the technology stack an incorrect choice, as it is secondary to SAP’s process-centric AI strategy.
Summary:
The unique elements ofSAP Business AIare its robust partner ecosystem with synergistic collaboration (leveraging partnerships with tech leaders and implementation partners), in-depth knowledge of business processes across various industries (enabling industry-specific AI use cases), and direct access to pertinent customer business data (using SAP’s enterprise data for reliable insights), corresponding to Options A, B, and E. Option C is incorrect because SAP does not develop SAP-specific LLMs, relying instead on partner models. Option D is incorrect because the focus is on business outcomes, not the technology stack. These elements align with SAP’s strategy to deliver relevant, reliable, and responsible AI withinSAP Business Suite, as supported by the provided search results and official documentation.
What are some essential value propositions of SAP Business AI? Note: There are 3 correct answers to this question.
Training of large multi-modal foundation models based on customer-specific business data
Use of the best technology on the market and strategic partnerships with industry leaders
Deployment of Joule, an advanced AI copilot, to help interpret business data and provide intelligent responses to business inquiries
Use of extensive business data extracted from areas including Finance, Supply Chain, Procurement, and Human Resources
Replacement of human workers with AI agents to reduce cost and human error
SAP Business AI is a suite of AI capabilities embedded across SAP’s enterprise applications, such as SAP S/4HANA, SAP SuccessFactors, and SAP Business Data Cloud, designed to enhance business processes, drive innovation, and deliver intelligent insights. The question asks for the essential value propositions of SAP Business AI, with three correct answers. Below, each option is evaluated based on official SAP documentation, SAP Learning materials, and relevant web sources from the provided search results, ensuring alignment with the "Positioning SAP Business Suite" and "SAP Business AI" narratives.
Option A: Training of large multi-modal foundation models based on customer-specific business dataSAP Business AI focuses on embedding pre-trained AI models and generative AI capabilities into business applications, leveraging SAP’s extensive business data and integrations like SAP Databricks. However, the documentation does not emphasize training large multi-modal foundation models based on customer-specific data as a core value proposition. Instead, SAP prioritizes using existing models, fine-tuned with business context, to deliver out-of-the-box value. Training custom foundation models is more resource-intensive and not a primary focus of SAP’s AI strategy, which aims for rapid deployment and scalability.Extract: "SAP Business AI embeds intelligent capabilities directly into your business processes, so you can work faster, smarter, and more efficiently. From automating routine tasks to providing predictive insights, AI is seamlessly integrated into SAP applications to drive better outcomes." This option is incorrect.
Option B: Use of the best technology on the market and strategic partnerships with industry leadersA key value proposition of SAP Business AI is its use of cutting-edge technology and strategic partnerships with industry leaders like Microsoft, Google Cloud, and Databricks. These partnerships enhance SAP’s AI capabilities, enabling advanced analytics, generative AI, and seamless integration with leading AI platforms. SAP’s collaboration with these partners ensures that customers benefit from state-of-the-art technology, making this a prominent value proposition in the documentation and marketing materials.Extract: "SAP Business AI leverages the best AI technology on the market, powered by strategic partnerships with industry leaders like Microsoft, Google Cloud, and Databricks. These collaborations ensure that our customers have access to cutting-edge AI capabilities, seamlessly integrated into their SAP applications." Extract: "The partnership between SAP and Databricks enables customers to combine the benefits of SAP Business Data Cloud with Databricks’ powerful AI and ML capabilities, delivering unparalleled value through advanced analytics and AI." This option is correct.
Option C: Deployment of Joule, an advanced AI copilot, to help interpret business data and provide intelligent responses to business inquiriesThe deployment of Joule, SAP’s advanced AI copilot, is a central value proposition of SAP Business AI. Joule is embedded across SAP applications to provide conversational AI, interpret business data, and deliver intelligent, context-aware responses to user inquiries. It enhances productivity by automating tasks and providing insights in natural language, making it a key feature highlighted in SAP’s AI strategy.Extract: "Joule, SAP’s advanced AI copilot, is embedded across our portfolio to help users interpret complex business data, automate tasks, and respond to inquiries with intelligent, context-aware answers. Joule transforms how businesses operate by delivering AI-driven productivity." Extract: "With SAP Business AI and Joule, customers can ensure accurate results from generative AI, augmenting decision-making with conversational AI and improving productivity through automated workflows." This option is correct.
Option D: Use of extensive business data extracted from areas including Finance, Supply Chain, Procurement, and Human ResourcesSAP Business AI leverages extensive business data from core areas like Finance, Supply Chain, Procurement, and Human Resources, extracted from SAP applications such as SAP S/4HANA and SAP SuccessFactors. This rich, semantically contextual data is a critical value proposition, enabling AI to deliver relevant, business-specific insights and drive intelligent automation. The documentation emphasizes the power of SAP’s data foundation as a differentiator for its AI offerings.Extract: "SAP Business AI is powered by extensive business data from SAP applications, including Finance, Supply Chain, Procurement, and Human Resources. This semantically rich data provides the context needed for AI to deliver precise, actionable insights tailored to your business." Extract: "Built-In Business Semantics: Because SAP data already carries deep business context and semantics, Databricks can provide powerful analytics and machine learning without forcing customers to re-invent data pipelines or guess at the meaning of fields." This option is correct.
Option E: Replacement of human workers with AI agents to reduce cost and human errorSAP Business AI focuses on augmenting human capabilities, not replacing human workers. The goal is to enhance productivity, automate repetitive tasks, and provide intelligent insights to support decision-making, while keeping humans in the loop. Replacing workers is not a value proposition of SAP Business AI, as it emphasizes collaboration between AI and human expertise. The documentation explicitly highlights augmentation over replacement.Extract: "SAP Business AI enhances human capabilities by automating routine tasks and providing predictive insights, allowing employees to focus on higher-value work. Our AI is designed to augment, not replace, human expertise." This option is incorrect.
Summary of Correct Answers:
B: SAP Business AI leverages the best technology and strategic partnerships with industry leaders to deliver cutting-edge AI capabilities.
C: Deployment of Joule, an advanced AI copilot, enhances productivity by interpreting business data and providing intelligent responses.
D: Using extensive business data from Finance, Supply Chain, Procurement, and Human Resources enables context-rich, actionable AI insights.
Match the challenges to their respective personas.
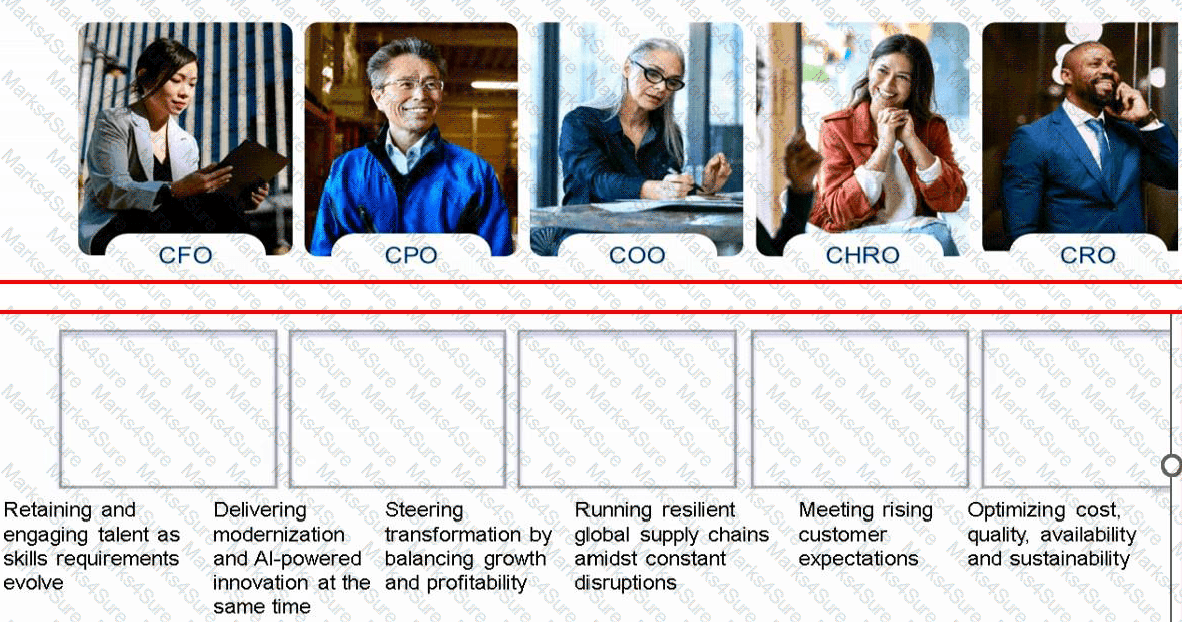
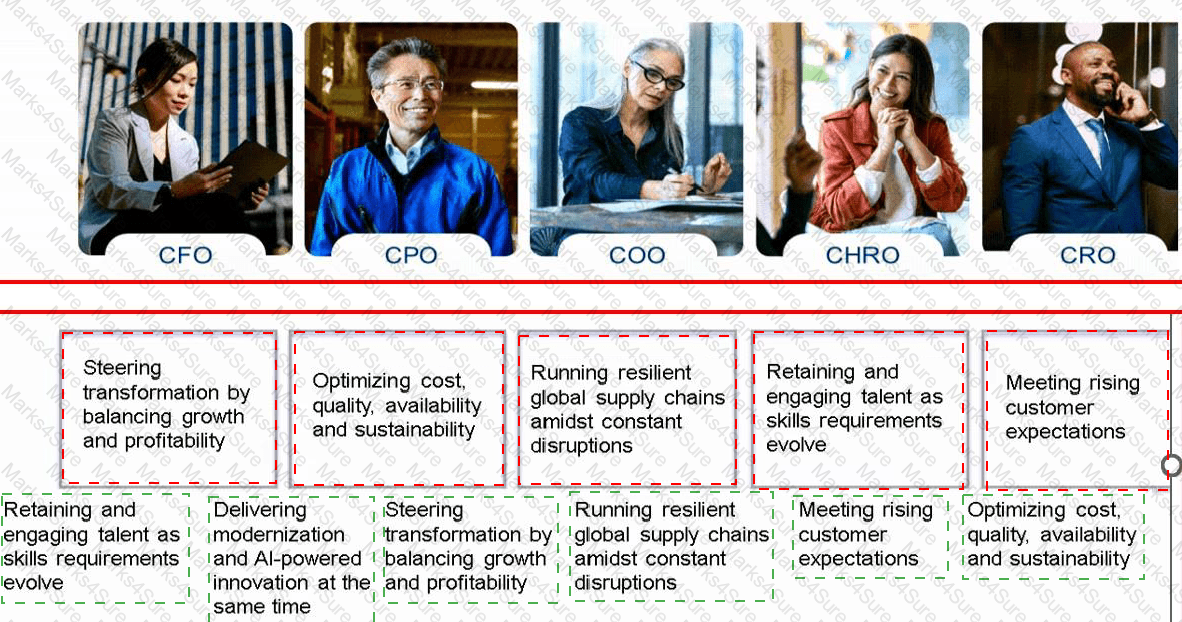
CFO:Steering transformation by balancing growth and profitability
CPO:Optimizing cost, quality, availability and sustainability
COO:Running resilient global supply chains amidst constant disruptions
CHRO:Retaining and engaging talent as skills requirements evolve
CRO:Meeting rising customer expectations
CIO:Delivering modernization and AI-powered innovation at the same time

TESTED 29 Jan 2026

